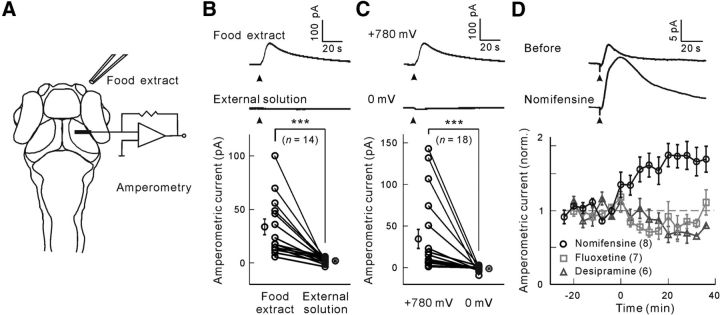
Figure 1.
C-fiber microelectrode-based amperometric measurement of food extract-evoked dopamine release at the OT in awake larval zebrafish. A, Experimental paradigm. A C-fiber microelectrode was placed in the neuropil of the OT, and food extract was applied pneumatically at the ipsilateral nostril through a glass micropipette. B, Amperometric current responses evoked by application (arrowhead) of food extract or external solution when the C-fiber microelectrode was held at 780 mV. Top, Sample trace showing food extract-evoked response. Middle, Sample trace showing external solution-evoked response. Bottom, Summary. Each symbol represents data obtained from individual larvae, and the data obtained from the same larva are connected by a line. C, Amperometric current responses evoked by food extract (arrowhead) when the C-fiber microelectrode was held at 780 or 0 mV. Top, Sample trace at 780 mV. Middle, Sample trace at 0 mV. Bottom, Summary. Each symbol represents data obtained from individual larvae, and the data obtained from the same larva are connected by a line. D, Amperometric current responses evoked by food extract when the larva was treated with the dopamine reuptake blocker nomifensine (32 μm), the serotonin reuptake blocker fluoxetine (0.8 μm), or the norepinephrine reuptake blocker desipramine (165 μm). Top, Sample traces before and after bath application of nomifensine. Bottom, Mean changes with time. The drugs were applied at time 0. ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate SEM.