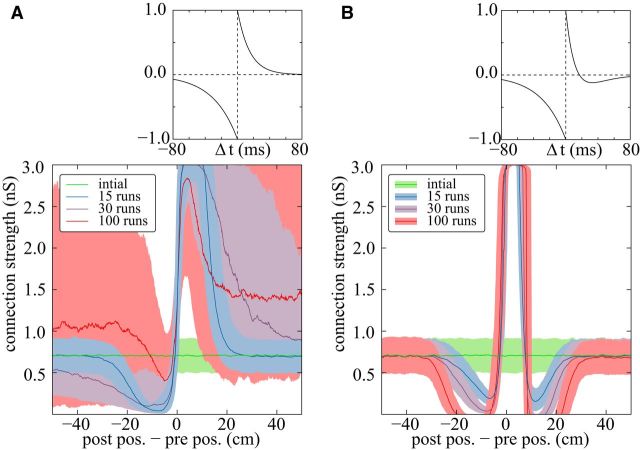
Figure 5.
Alternative STDP kernel generating stable learning dynamics for large numbers of runs. A, B, Top, STDP time windows (compare Eqs. 9 and 26); bottom, distributions of weights versus the distances of the place-field centers of postsynaptic and presynaptic neurons (compare Fig. 4D). A, A standard STDP window (compare Eqs. 9–11) results in more prominent feedforward substructures for more runs along the linear track. After a large number of runs, replay events are initiated even during the exploration phase and cause pathological activity, which amplifies the connection strengths even more. B, A different STDP window where causal spiking induces depression for larger Δt yields stable learning dynamics (compare Eq. 26, with A = 8, τx = 17 ms and α = 0.18; other parameters as before). As in A, a prominent feedforward structure forms, but the depression for large Δt confines strong connections to neurons with nearby place fields and thus prevents overlearning and pathological activity states.