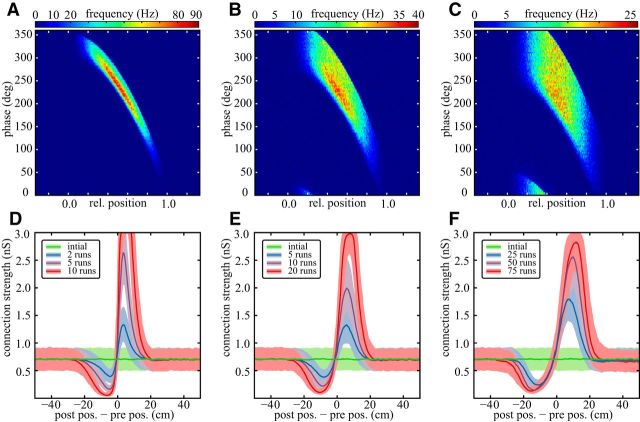
Figure 6.
Impact of unreliable spiking phase. A–C, Spatiotemporal receptive fields with different widths (A, Δτ = 20 ms, Imax = 500 pA; B, Δτ = 40 ms, Imax = 340 pA; C, Δτ = 60 ms, Imax = 280 pA). The underlying theta oscillation has a frequency of 8 Hz. D–F, Distribution of synaptic weights as a function of the distance between the place field centers of the postsynaptic and the presynaptic neuron after multiple runs along the linear track with phase precession given by the receptive field above. The running speed is v̄ = 8 cm/s, and the place-field width is Δw = 40 cm. Broader distributed, more unreliable phase shifts do not qualitatively change the feedforward structure formation. It only requires more runs, because the actual spiking times have less reliable order and temporal difference.