Figure 1.
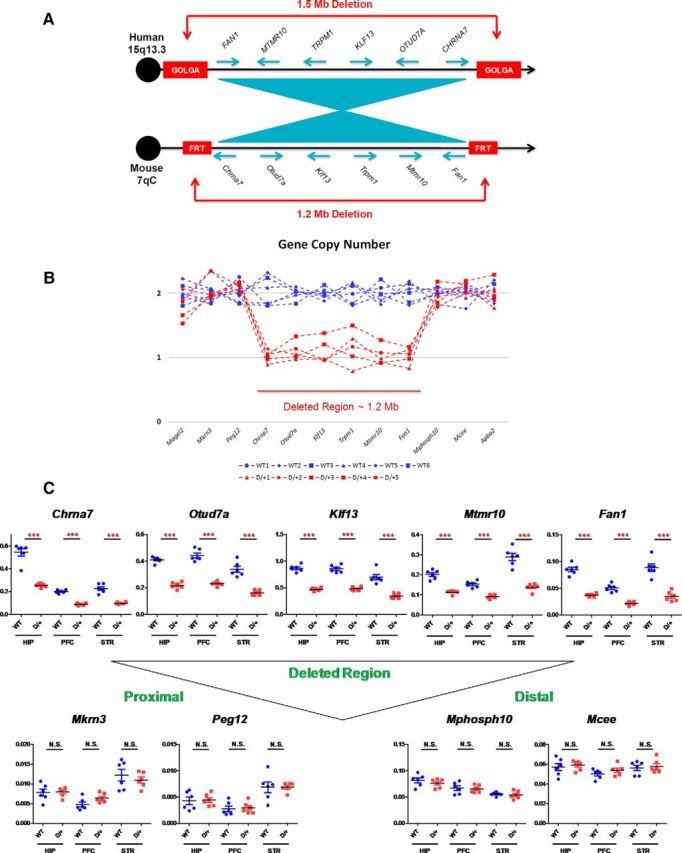
Generation of 15q13.3 microdeletion mouse model (D/+ mice). A, Gene content and order in the region commonly deleted in 15q13.3 microdeletion patients compared with that in a region of mouse chromosome 7. Note that the relative order of genes is conserved but with inverted centromere–telomere orientation. Blue arrows indicate the transcriptional orientation of genes. In humans, commonly observed 1.5 Mb deletion in 15q13.3 region arises through nonallelic homologous recombination between duplication blocks, which harbor copies of the GOLGA gene family. In mice, artificial FRT sites were inserted into regions corresponding to human GOLGA-containing duplication blocks to induce cis-recombination mediated 1.2 Mb deletion. B, Gene copy number in the deleted region and flanking regions. C, Gene expression levels in the hippocampus (HIP), prefrontal cortex (PFC), and striatum (STR). Levels of gene expression were normalized by Gapdh levels. ***p < 0.001; N.S., Nonsignificant.
