Figure 8.
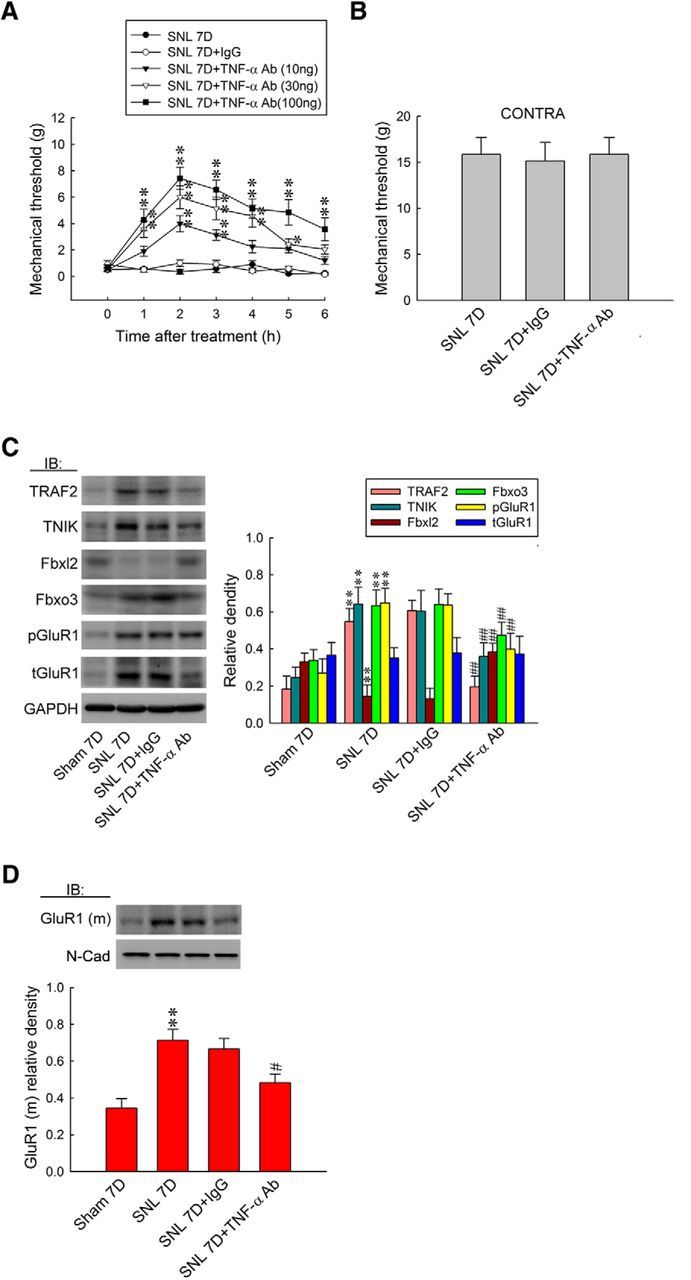
TNF-α-neutralizing antibody relieves allodynia by attenuating spinal Fbxo3/Fbxl2/TRAF2/TNIK/pGluR1-dependent GluR1–AMPAR trafficking. A, B, Intrathecal administration with an TNF-α-neutralizing antibody (SNL 7D+TNF-α Ab; 10, 30, and 100 ng, 10 μl), but not nonspecific IgG (SNL 7D+IgG; 100 ng, 10 μl), dose dependently increased the withdrawal threshold of the ipsilateral hindpaw. In addition, neither treatment affected the contralateral hindpaw at 2 h after injection (TNF-α-neutralizing antibody, 100 ng; von Frey test). Ipsilateral hindpaw, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures over time: treatment, F(4,30) = 64.39, p < 0.001; time, F(6,180) = 24.44, p < 0.001; treatment × time, F(24,180) = 4.657, p < 0.001. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus SNL 7D. n = 7. Contralateral hindpaw, one-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey's test: F(2,18) = 0.047, p = 0.954. C, D, Although it had no effect on tGluR1, administrating with TNF-α-neutralizing antibody reversed SNL-upregulated TRAF2, TNIK, Fbxo3, pGluR1, GluR1(m), and SNL-downregulated Fbxl2 (normalized to GAPDH or N-cadherin) expressions. One-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey's test: TRAF2, F(3,20) = 75.39, p < 0.001; TNIK, F(3,20) = 29.62, p < 0.001; Fbxl2, F(3,20) = 34.78, p < 0.001; Fbxo3, F(3,20) = 22.30, p < 0.001; pGluR1, F(3,20) = 24.55, p < 0.001; tGluR1, F(3,20) = 0.086, p = 0.966; GluR1(m), F(3,20) = 10.10, p < 0.001. **p < 0.01 versus Sham 7D. ##p < 0.01 versus SNL 7D. n = 6.
