Figure 4.
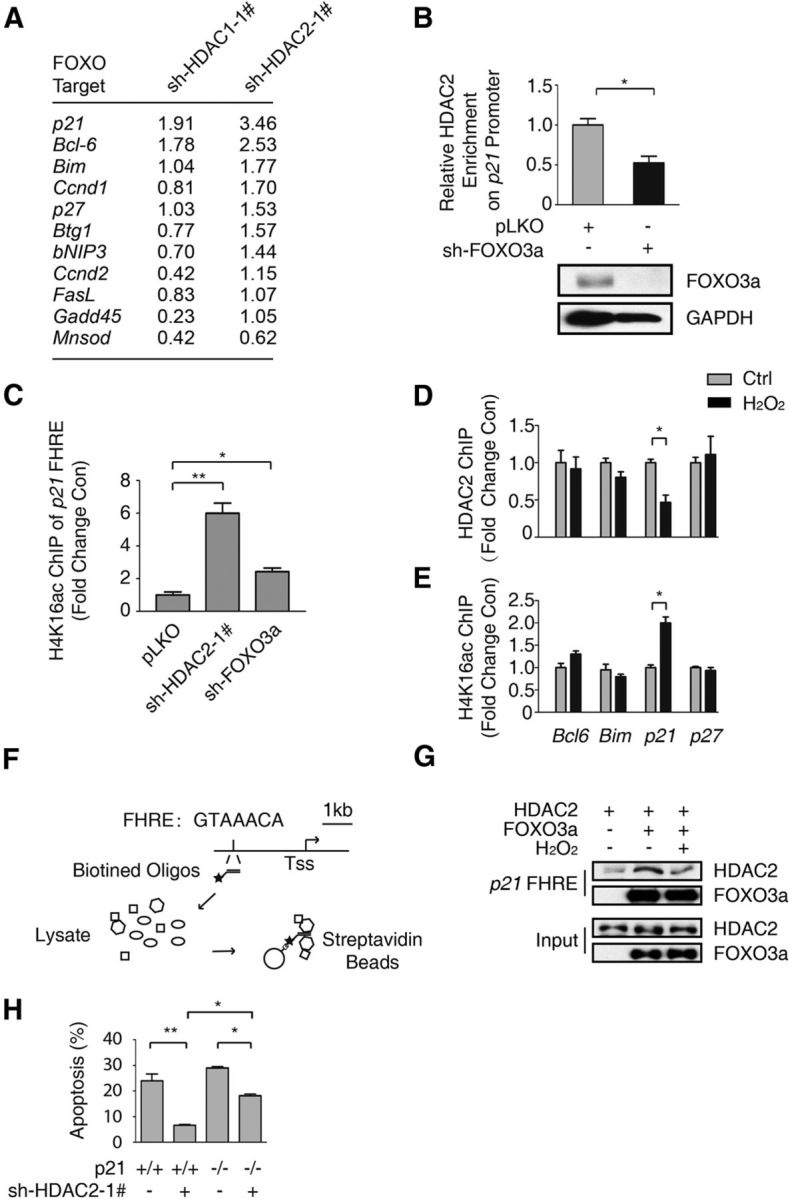
HDAC2 is recruited to the p21 promoter by FOXO3a and regulates p21 expression. A, Total RNA was extracted from HT-22 cells with HDAC1 or HDAC2 stably knocked down. The relative mRNA level was detected via qRT-PCR. The fold-change in the RNA level compared with pLKO empty cells was determined. B, HT-22 cells with FOXO3a stably knocked down and control HT-22 cells were subjected to ChIP using an anti-HDAC2 antibody. qRT-PCR was performed to detect the abundance of HDAC2 at the p21 FHRE (top). The HDAC2 abundance was decreased due to FOXO3a knockdown (Student's t test, n = 3; *p < 0.05). Lysates from FOXO3a knockdown and pLKO-transfected control HT-22 cells were immunoblotted using anti-FOXO3a and anti-GAPDH antibodies (bottom). C, Lysates from HT-22 cells with HDAC2 or FOXO3a stably knocked down and pLKO control HT-22 cells were subjected to ChIP using an anti-H4K16ac antibody. The p21 promoter acetylation level was analyzed via qRT-PCR using primers specific to the p21 FHRE. HDAC2 knockdown (Student's t-test, n = 3, **p < 0.01) and FOXO3a knockdown (Student's t-test, n = 3, *p < 0.05) promoted H4K16ac enrichment in the p21 promoter. D, HT-22 cells were treated with 0 or 300 μm H2O2 for 1 h. Then, the samples were subjected to ChIP using the anti-HDAC2 antibody, which was followed by qRT-PCR analysis of the Bcl6, Bim, p21, and p27 promoter FHRE regions. HDAC2 was specifically enriched in the p21 promoter (Student's t test, n = 3; *p < 0.05). E, HT-22 cells were treated with 0 or 300 μm H2O2 for 1 h. Then, the samples were subjected to ChIP using an anti-H4K16ac antibody, which was followed by qRT-PCR analysis of the Bcl6, Bim, p21, and p27 promoter FHRE regions. The H4K16ac level was increased in the p21 promoter (Student's t test, n = 3, *p < 0.05). F, Flow chart of the DNA pull-down assay for the p21 FHRE. G, 293T cells were transfected with the Flag-HDAC2 or Flag-FOXO3a expression plasmid. The cells were treated with 300 μm H2O2 for 1 h before they were harvested, as indicated. The cell lysates were pulled down using the biotin-labeled p21 FHRE. Western blotting was performed using an anti-HDAC2 antibody. H, CGNs prepared from WT or p21 knock-out mice were transfected with pEGFP-N1 together with the pLKO-HDAC2–1# plasmid, as indicated. The neuronal apoptosis assay was performed as in Figure 2A. The neuronal protection of HDAC2 knockdown in p21−/− CGNs was less than in WT CGNs (ANOVA, n = 4 for each group; *p < 0.05).
