Figure 8.
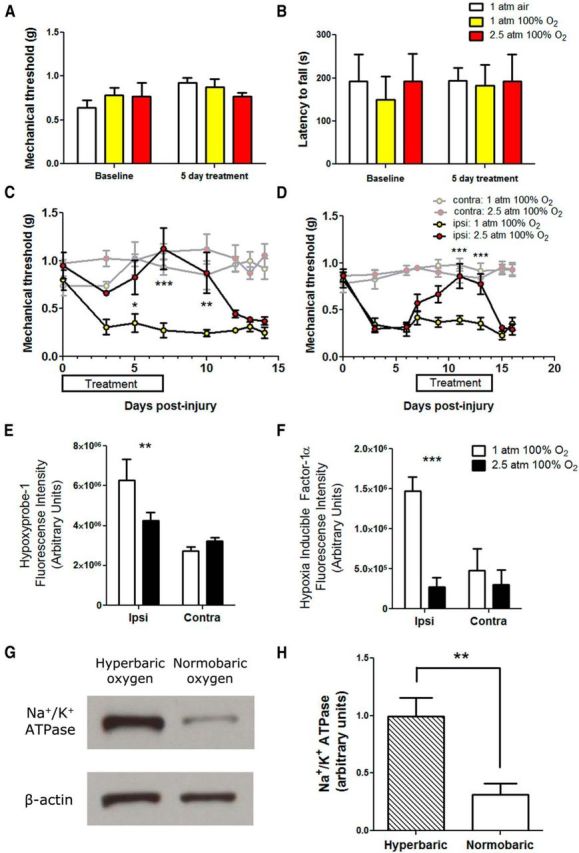
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment alleviates painful peripheral neuropathy induced by traumatic injury. A, Naive animals were exposed to air, normobaric oxygen, or hyperbaric oxygen, and mechanical thresholds were measured. There was no significant differences of either treatment condition on mechanical thresholds. B, Motor responses were also measured by the rotarod test. Normobaric oxygen or hyperbaric oxygen had on effects of motor responses on naive animals. C, After PSNL, mice received hyperbaric oxygen (100% O2 at 2.5 atm) or sham treatment (100% O2 at 1 atm) for 2 h daily, from day 0 to day 7 after injury. Hyperbaric oxygen significantly alleviated mechanical allodynia (n = 5 per group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). Contralateral mechanical thresholds were not altered by hyperbaric or normobaric oxygen treatment. D, Hyperbaric oxygen administered from day 7 to day 14 after injury was also able to significantly alleviate mechanical allodynia (n = 5 per group; ***p < 0.001). Hyperbaric or normobaric oxygen treatment did not alter contralateral mechanical thresholds. E, Hyperbaric oxygen treatment from day 0 to day 7 after injury significantly reduced the amount of hypoxyprobe-1 adducts observed in injured nerve at day 7 (n = 3 per group; **p < 0.01). F, Hyperbaric oxygen treatment from day 0 to day 7 after injury significantly reduced the amount of immunoreactivity in HIF-1α-stained nerve sections (n = 3 per group; ***p < 0.001). G, Example immunoblots of pan Na+/K+ ATPase and β-actin in sciatic nerve lysates from ipsilateral nerves from animals that received hyperbaric oxygen or sham treatment (normobaric oxygen). H, Hyperbaric oxygen treatment from day 0 to day 7 after injury significantly increased the amount of Na+/K+ ATPase α protein levels in injured nerves as determined by Western blot (n = 6–8 per group; **p < 0.01).
