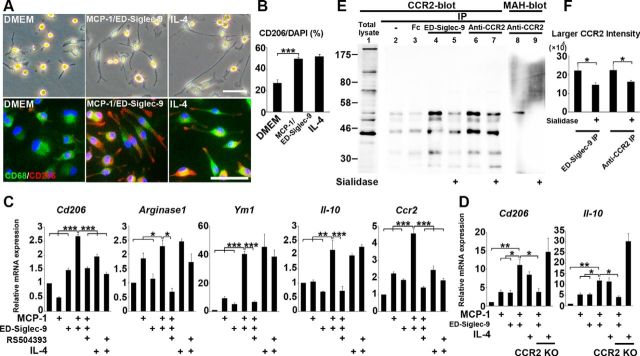
Figure 4.
MCP-1 and ED-Siglec-9 synergistically induce M2-like macrophages via CCR2. A, Representative images of rat primary BMMs treated with DMEM, 100 ng/ml MCP-1/ED-Siglec-9, or 20 ng/ml IL-4. Top, Optical-microscopy images; bottom, CD206/CD68/DAPI immunostaining. B, Quantification of CD206+/DAPI macrophages. ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test (n = 3 separate experiments). C, D, Quantitative mRNA expression analysis of the indicated genes. BMMs treated with MCP-1/ED-Siglec-9 or IL-4. Results are relative to DMEM treatment. C, BMMs treated with or without CCR2 antagonist RS504393 (50 μm). D, BMMs from adult CCR2 KO mouse. CCR2 inhibition suppressed the MCP-1/ED-Siglec-9 mediated M2 differentiation but did not affect IL-4-mediated M2-induced signaling. ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test (n = 3 separate experiments). E, THP-1 cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using antibodies against ED-Siglec-9 or CCR2, and the precipitates were immunoblotted with anti-CCR2 antibody or MAH lectin (see Results). ED-Siglec-9 physically interacted with the larger, sialylated CCR2 (lane 4). Sialidase treatment suppressed the physical interaction between larger CCR2 and ED-Siglec-9 (lane 5). F, Quantitative analysis showing that sialidase treatment inhibited the interaction of larger CCR2-ED-Siglec-9 (lane 5). ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test (n = 3 separate experiments). Scale bar: A, 50 μm. Mean ± SD (B, F) and mean ± SEM (C, D). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.