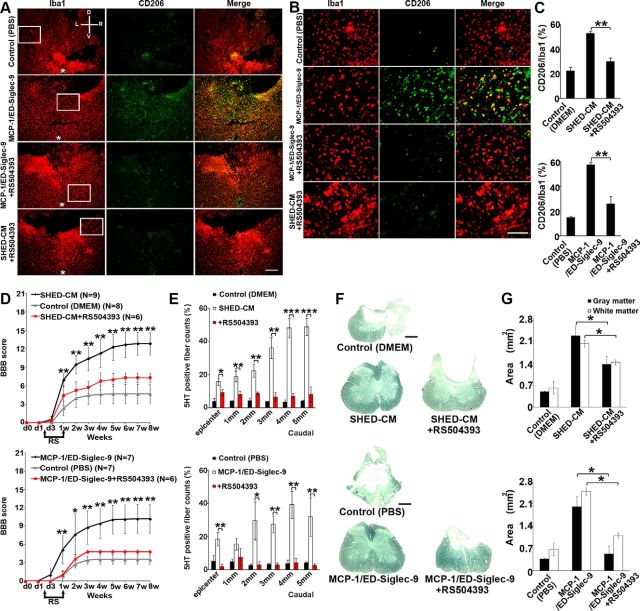
Figure 8.
Effects of CCR2 depletion on MCP-1/ED-Siglec-9-stimulated M2 induction. A selective inhibitor for CCR2, RS504393 (2 mg/kg), was given to rats orally every 12 h for 1 week starting 36 h after SCI. A, B, Representative immunohistological images of axial plane spinal cord sections 3 mm caudal to the epicenter 72 h after SCI. Left, Treatment; top, antibodies. D, Dorsal; V, ventral; L, left; R, right. Asterisks in the left indicate the central canal of the spinal cord. B, High-power view of the boxed area in A. C, Quantitative analysis. ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test (n = 3 rats per group and 5 sections per animal). SHED-CM or MCP-1/ED-Siglec-9 failed to induce CD206+ M2-like cells in the SCI rat treated with RS504393. D, Recovery of hindlimb locomotion after SCI. Top, SHED-CM, n = 9; DMEM, n = 8; SHED-CM + RS504393, n = 6. Bottom, MCP-1/ED-Siglec-9, n = 7; PBS, n = 7; MCP-1/ED-Siglec-9 + RS504393, n = 6. ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test. E, Quantification of 5-HT-positive nerve fibers from the epicenter to 5 mm caudal. ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test (n = 3 rats per group and 5 sections per animal). F, G, Sudan black B staining of axial spinal cord sections 3 mm caudal to the epicenter 8 weeks after SCI, and quantification of gray and white matter areas 3 mm caudal to the epicenter. ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test (n = 3 rats per group). Scale bars: A, 200 μm; B, 100 μm; F, 500 μm. Mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. RS, RS504393.