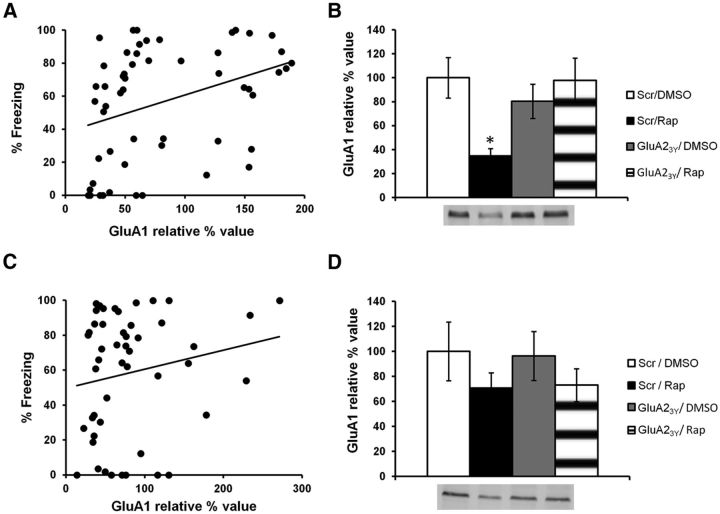
Figure 5.
Infusion of rapamycin decreases levels of GluA1 at the PSD, but not at extrasynaptic sites. Rats were trained in an auditory fear-conditioning task and received an infusion of GluR23Y and rapamycin (GluA23Y/Rap; n = 12), scrambled-GluA23Y and rapamycin (Scr/Rap; n = 17), GluA23Y and DMSO (GluA23Y/DMSO; n = 12), or vehicle (Scr/DMSO; n = 13). A, Results show a significant positive correlation between the percentage of time spent freezing in the memory retrieval test and levels of GluA1 at the PSD. B, Rats infused with rapamycin showed significantly lower GluA1 levels than all other groups. C, D, No significant correlation (C) or significant differences in GluA1 levels (D) were found at extrasynaptic sites. Levels of GluA1 are expressed as relative percentage values of the vehicle group ± SEM. *p < 0.05.