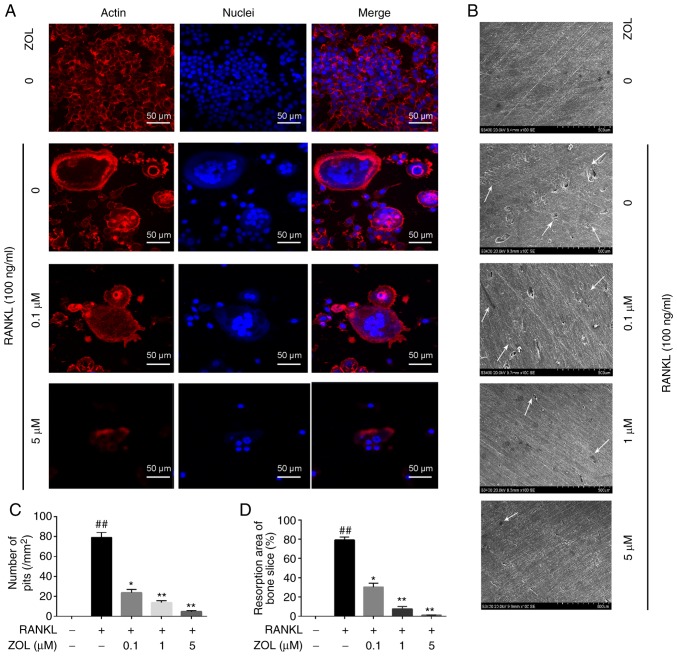
Figure 3.
ZOL inhibits RANKL-induced gathering of nuclei, F-actin ring formation and bone resorptive activity. (A) RAW264.7 cells were treated with various concentrations of ZOL in the presence or absence of 100 ng/ml RANKL until mature osteoclasts were observed. Cell nuclei and F-actin rings were stained with DAPI and TRITC phalloidin, respectively. Fluorescence was detected by using a confocal microscope. (B) RAW264.7 cells were treated with various concentrations of ZOL in the presence or absence of 100 ng/ml RANKL until mature osteoclasts formed. Bone resorption pits (indicated by white arrows) were visualized under a scanning electron microscope. (C) The number of pits and (D) the resorption area was determined. ##P<0.01 vs. the vehicle group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. the RANKL-only group. ZOL, zoledronic acid; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear-κB ligand.