Figure 1.
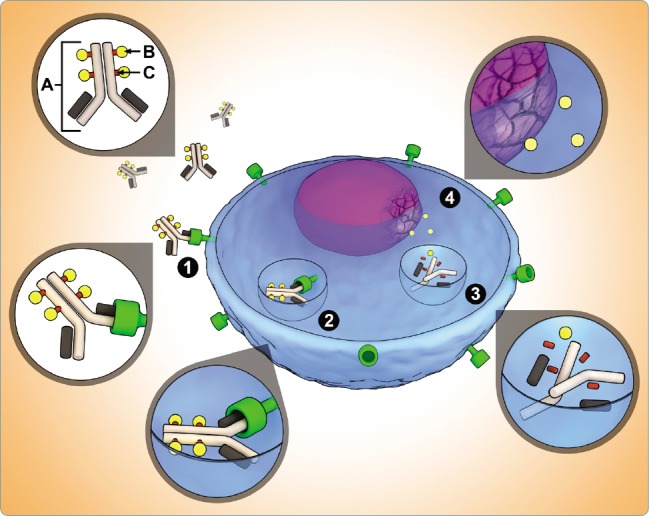
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) structure and mechanism of action. The ADC consists of three key components: (A) site-specific monoclonal antibody; (B) cytotoxic drug; and (C) functional linker that binds drug to antibody. ADC mechanism of action: (1) binding of ADC to antigen of cancer cell; (2) internalization of antigen-ADC complex; (3) lysosomal degradation releases drug from antibody; (4) drug causes DNA or microtubule disruption. From "Antibody-drug conjugates: A clinical pharmacy perspective on an emerging cancer therapy," by Jerjian et al., 2016, Pharmacotherapy, 36(1), 99–116. © 2016 Pharmacotherapy Publications, Inc. Reprinted with permission.
