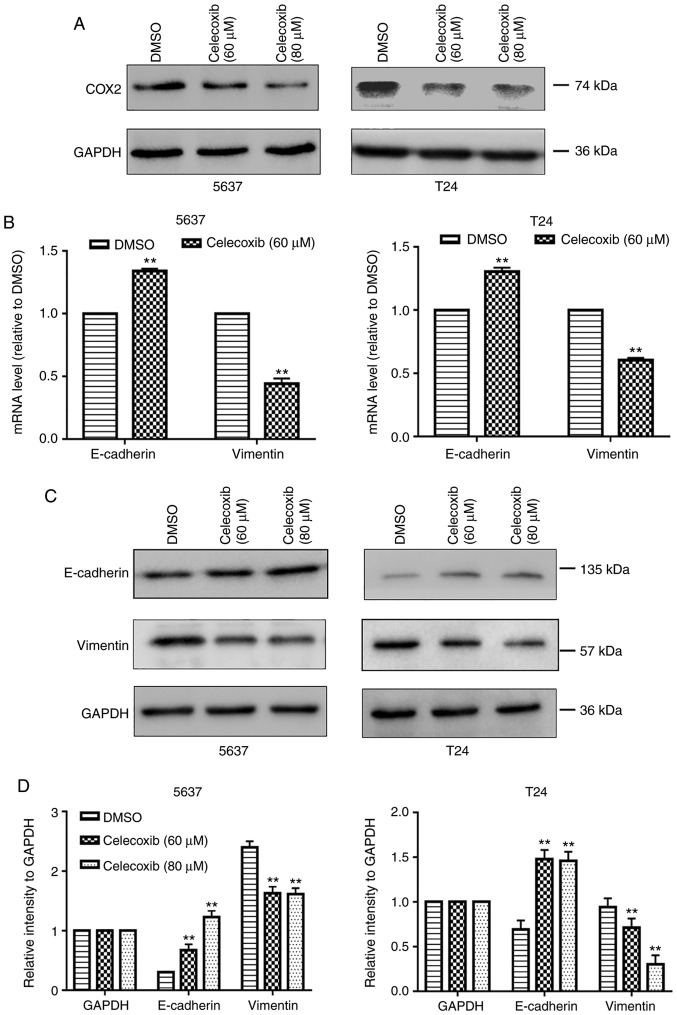
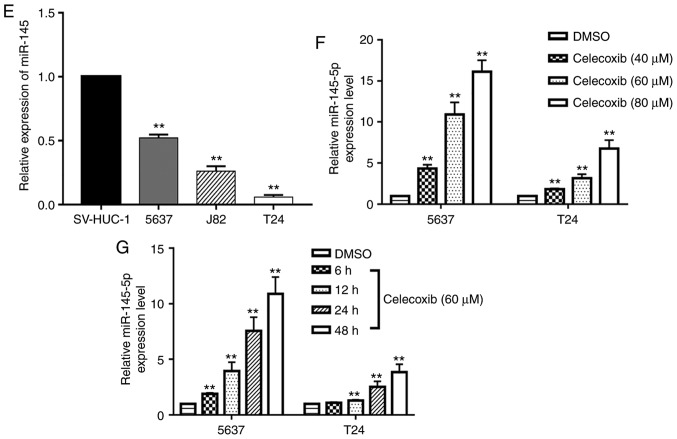
Figure 2.
Celecoxib inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and upregulates miR-145 in bladder cancer cells. 5637 and T24 bladder cancer cells were treated with DMSO or celecoxib (60 or 80 µM) for 48 h. (A) Protein expression of COX-2 in 5637 and T24 cells subsequent to treatment with celecoxib were detected by western blot analysis. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (B) mRNA expression levels of E-cadherin and Vimentin were examined using RT-qPCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (C) Protein expression levels of E-cadherin and Vimentin in 5637 and T24 cells were detected by western blot analysis and (D) quantified. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Celecoxib inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and upregulates miR-145 in bladder cancer cells. (E) Expression levels of miR-145 in bladder cancer cell lines, as detected by RT-qPCR. SV-HUC-1 was used as a normal control. Effect of celecoxib on the expression levels of miR-145 in (F) dose-dependent and (G) time-dependent manners. Expression levels of miR-145 in 5637 and T24 cells following treatment with celecoxib were detected by RT-qPCR. U6 was used as an internal control. The data represent the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. **P<0.05 vs. the DMSO group. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; COX2, cyclooxygenase-2; miR, microRNA; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.