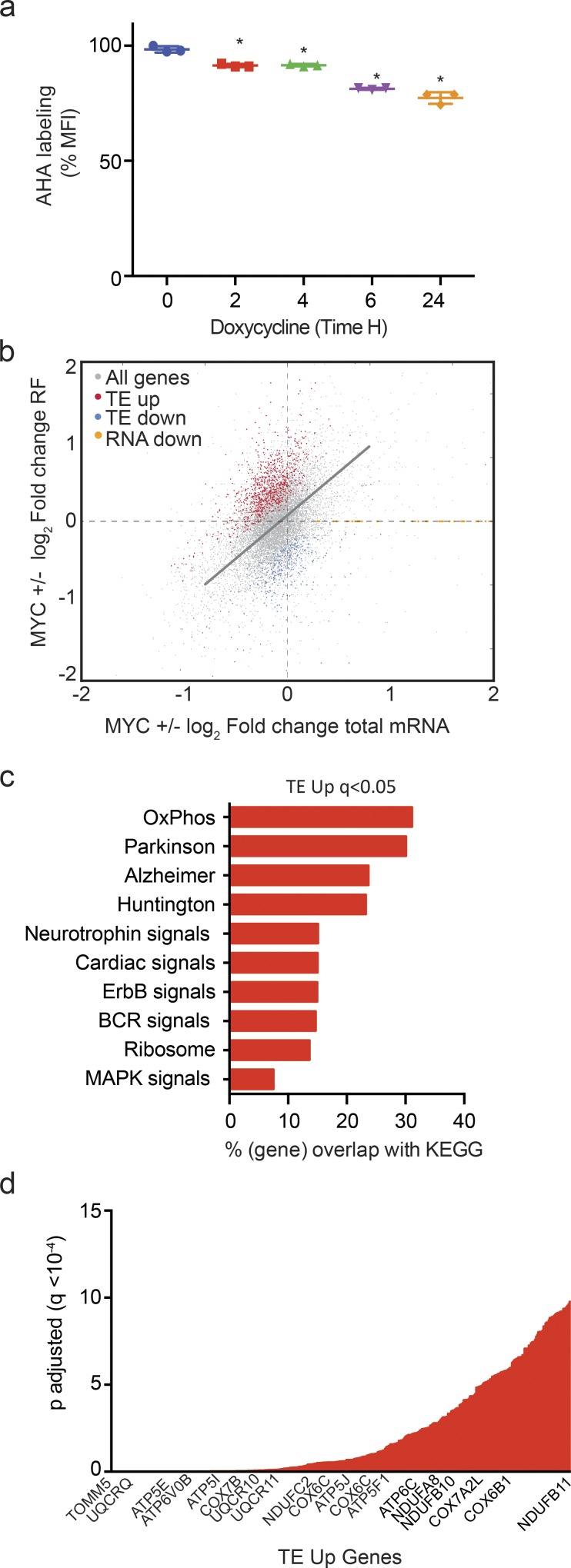
Figure 1.
MYC has specific effects on mRNA translation. (a) Metabolic labeling of newly synthesized proteins with AHA in P493-6 cells treated with doxycycline (0.1 µg/ml) for the indicated time period measured by FACS (n = 3 biological replicates, mean ± SD from three replicates, data representative of three independent experiments). P values were calculated using an unpaired Student’s t test: *, P ≤ 0.05. (b) Change in total mRNA levels versus change in RF reads in the presence or absence of MYC in P493-6 cells. The linear function indicates proportional changes in both: genes with a significantly (q < 0.01) disproportional increase in TE (TE up, red) or decrease (TE down, blue). Ribosome footprinting was performed in three biological replicates for each group. (c) GO analysis of pathways enriched in TE-up genes (q < 0.05); n = 3 biological replicates in each group; q values were calculated using the FDR method of Benjamini and Hochberg. (d) mRNAs whose translation was stimulated by MYC (TE up) ranked by significance (q < 0.05); n = 3 biological replicates in each group.