Figure 1.
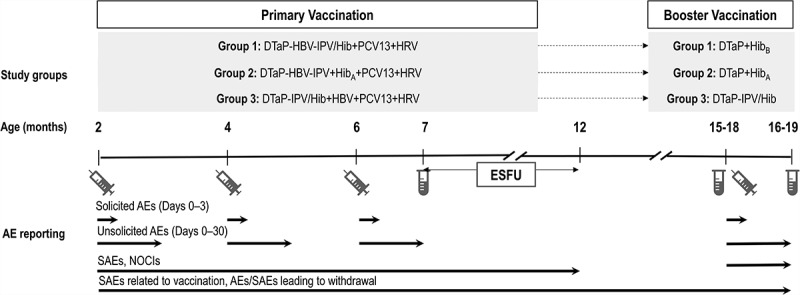
Study design.
 , vaccination;
, vaccination;  , blood sampling; DTaP-HBV-IPV/Hib, diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliovirus, and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine; DTaP-HBV-IPV, diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, and inactivated poliovirus vaccine; DTaP-IPV/Hib, diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, inactivated poliovirus, and Hib vaccine; DTaP, diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis vaccine; PCV13, 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; HRV, human rotavirus vaccine, administered at 2 and 4 months of age only; HBV, hepatitis B vaccine (not given at 4 months of age if a dose was administered at birth or 30 days prior to enrollment); HibA, HibB, monovalent Hib conjugate vaccines; AE, adverse event; SAE, serious adverse event; NOCIs, new onset of chronic illnesses; ESFU, extended safety follow-up.Infants in Group 1 received one of three lots of DTaP-HBV-IPV/Hib, but these three groups were pooled for all analyses presented here. The final randomization scheme was (1:1:1):3:3.
, blood sampling; DTaP-HBV-IPV/Hib, diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliovirus, and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine; DTaP-HBV-IPV, diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, and inactivated poliovirus vaccine; DTaP-IPV/Hib, diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, inactivated poliovirus, and Hib vaccine; DTaP, diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis vaccine; PCV13, 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; HRV, human rotavirus vaccine, administered at 2 and 4 months of age only; HBV, hepatitis B vaccine (not given at 4 months of age if a dose was administered at birth or 30 days prior to enrollment); HibA, HibB, monovalent Hib conjugate vaccines; AE, adverse event; SAE, serious adverse event; NOCIs, new onset of chronic illnesses; ESFU, extended safety follow-up.Infants in Group 1 received one of three lots of DTaP-HBV-IPV/Hib, but these three groups were pooled for all analyses presented here. The final randomization scheme was (1:1:1):3:3.
