Figure 4.
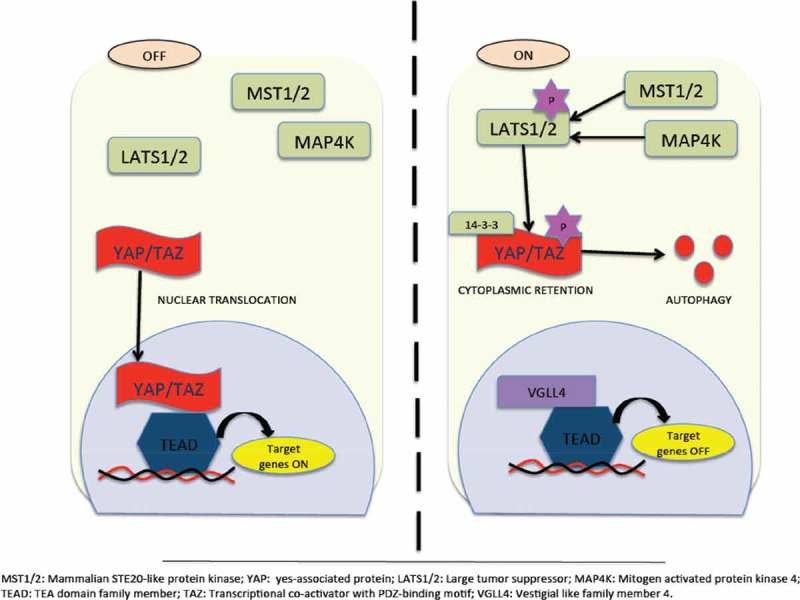
Hippo Pathway for tumor suppression. Inactivation of YAP/TAZ leads to oncogenic transcriptional module. Its inactivation is due to activation of hippo kinases MST1/2 that facilitates activation of LATS1/2 thereby phosporylating and retaining YAP/TAZ in the cytoplasm via 14–3-3 or being subjected to proteasomal or autophagy-induced degradation. Followed by this, suppression of TEAD-mediated gene transcription occurs. On the other hand, inactivation of hippo kinases occurs due to myriad reasons. Inactivation of hippo kinases leads to dephosphorylation of YAP/TAZ and translocates inside the nucleus inducing TEAD target gene expression. However, recent studies highlight Hippo-YAP-independent activation of TEAD too.77,78.
