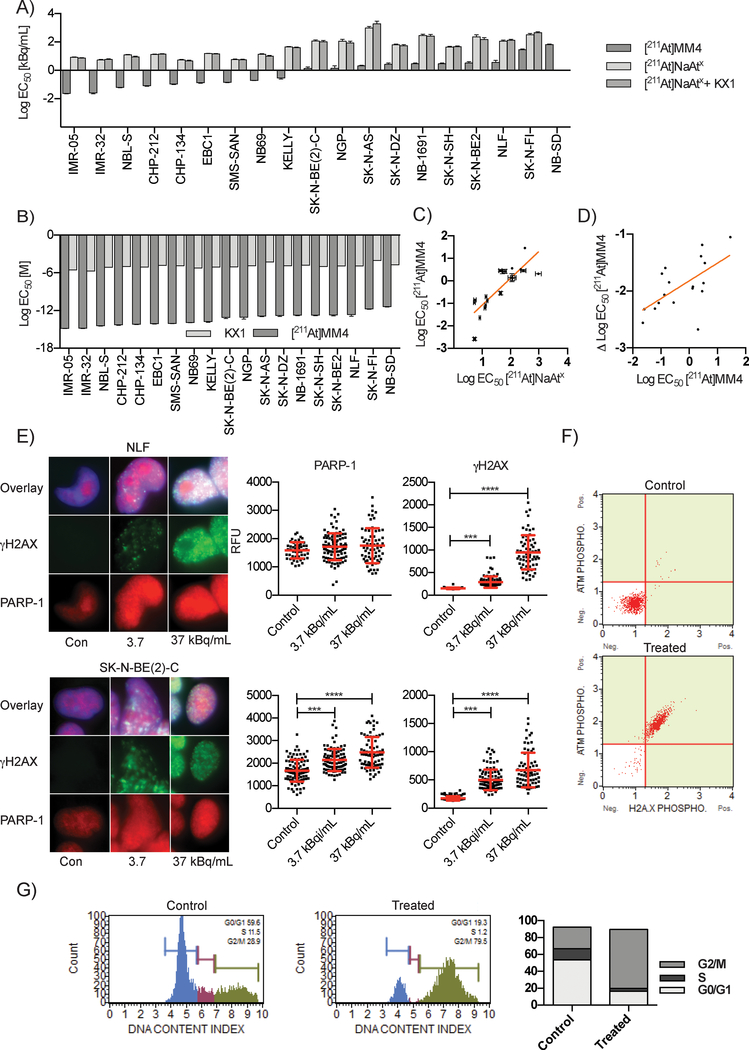
Figure 2:
In vitro studies evaluating [211At]MM4 cytotoxicity and DNA damage in neuroblastoma cell lines. A) Waterfall plot of EC50 values for a panel of 19 neuroblastoma cell lines that were used to test the in vitro cytotoxicity of [211At]MM4 vs. controls: free astatine-211 ([211At]NaAtx), and [211At]NaAtx with non-radioactive analogue PARP inhibitor KX1 (ANOVA p-value < 0.0001 for [211At]MM4 vs. controls in all cell lines). B) The comparison of EC50 values in molar units for [211At]MM4 vs. KX1 (ANOVA p- value < 0.0001 for all cell lines). C) Neuroblastoma cell line radiosensitivity correlation between [211At]MM4 and [211At]NaAtx (linear regression R2 = 0.708, p-value <0.0001 for non-zero slope). D) Neuroblastoma cell line radiosensitivity correlation between [211At]MM4 and [211At]MM4 normalized with [211At]NaAtx (linear regression R2 = 0.400, p-value <0.0033 for non-zero slope). E) Immunofluorescence of γH2AX and PARP-1 after 24 h treatment with [211At]MM4. PARP-1 was increased (t-test, p-value < 0.001) in SK-N-BE(2)-C cells and both cell lines showed increased γH2AX (t-test, p-value < 0.001). F) NLF cells treated with [211At]MM4 were analyzed by flow cytometry for ATM and H2AX phosphorylation. There was a 98% increase in ATM and H2AX phosphorylation in treated cells from control indicating double strand DNA breaks were the major form of DNA damage. G) Cell cycle analysis of NLF cells treated cells showed accumulation at the G2/M boundary.