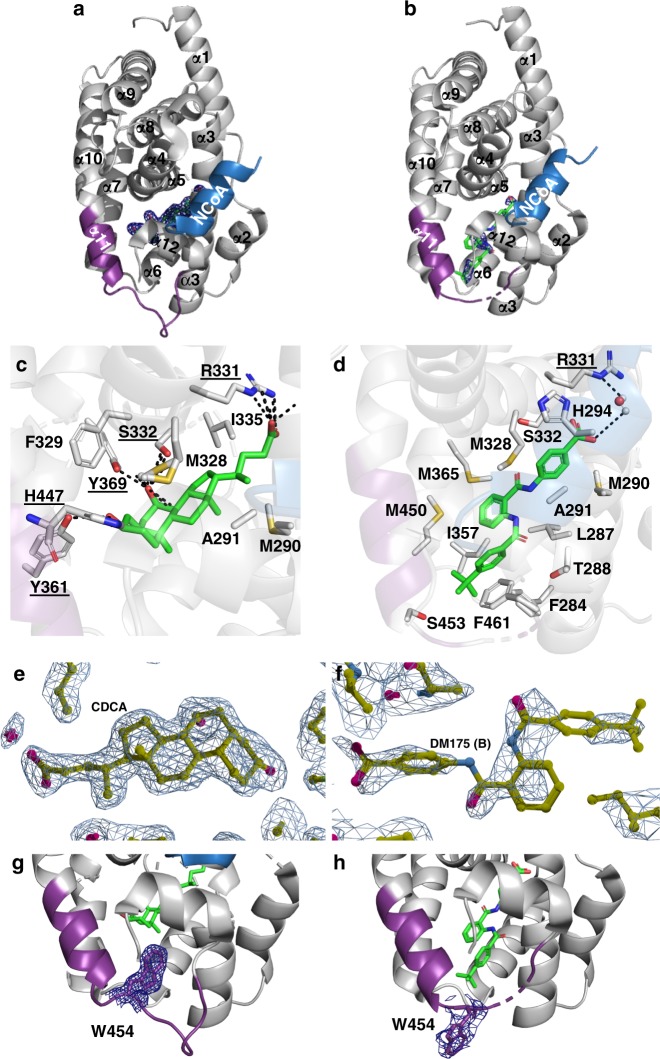
Fig. 2.
Binding modes of physiological FXR agonist CDCA and partial agonist 1 to the FXR-LBD. a CDCA bound to FXR. The co-activator (NCoA) is highlighted in blue. b Compound 1 bound to FXR. c, d Key residues involved in the interaction with CDCA and compound 1, respectively. e, f 2Fc-Fo omit maps (contour level 1.0 σ) for CDCA and compound 1 (chain B), respectively bound to the FXR-LBD. Chain B was considered for all interpretation due to preferable electron density for the ligand. Ligand density for chain A is poor due to twinning of the crystal. Additionally, the electron density of the loop region connecting α11 and α12 (V456-H459, AF-2 loop) in chain B is ambiguous or invisible, due to induced flexibility by binding of 1. g, h Compared to CDCA-bound FXR, binding of the partial agonist 1 causes an outward movement of W454 by 12 Å (2Fc-Fo omit maps, contour level 1.0 σ)