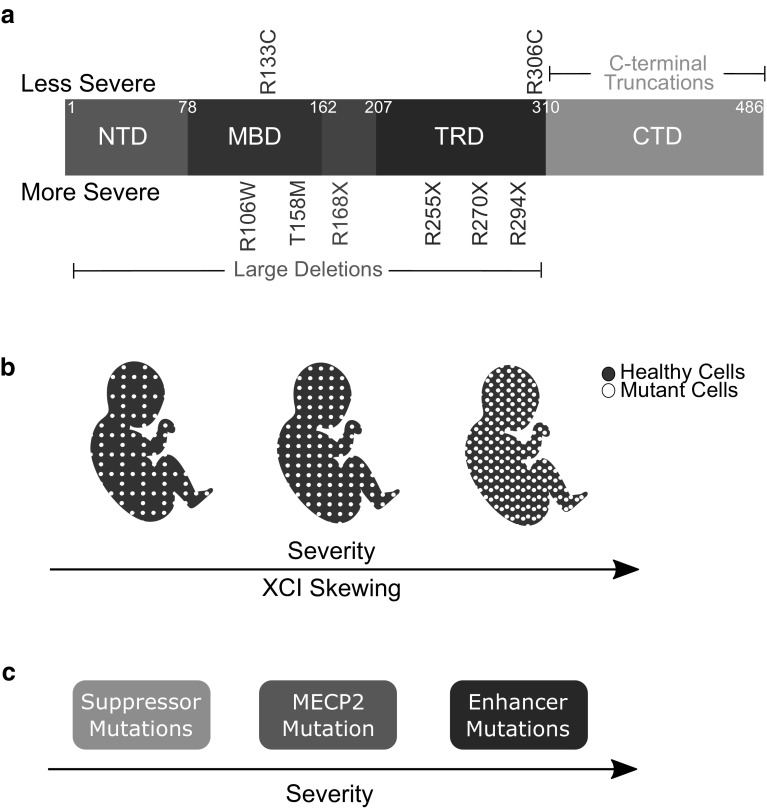
Fig. 1.
Symptom severity in RTT is influenced by mutation status, XCI pattern, and modifier genes. a Of the 8 most common RTT-causing MECP2 mutations, R133C and R306C cause the least severe clinical presentation, whereas the missense mutations R106W and T158M, and nonsense mutations R168X, R255X, R270X, and R294X cause the most severe phenotype. Large deletions in the MECP2 gene also cause a severe phenotype, whereas smaller C-terminal truncations are less severe. b Differences in XCI skewing patterns can influence clinical presentation, where patients with fewer cells expressing the mutant MECP2 gene will have less severe symptoms. c Individuals who have modifier mutations in genes that suppress the RTT phenotype have a more favorable clinical presentation than individuals with mutations in genes that enhance detrimental symptoms