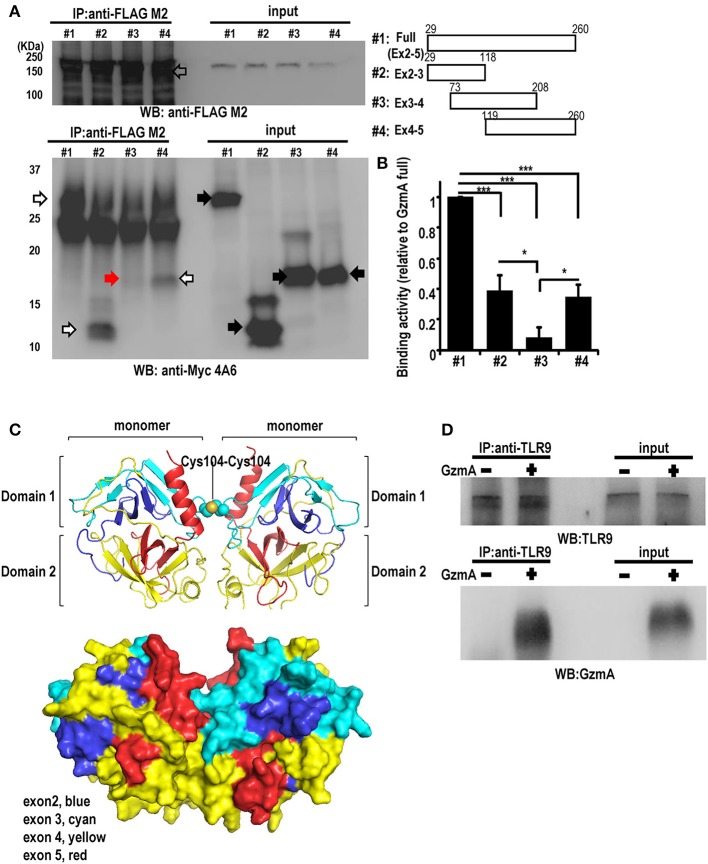
Figure 4.
Interaction between GzmA and TLR9. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation western blot (WB) assay for the interaction between GzmA and TLR9. cMyc-tagged full-length or truncated GzmA proteins (right) and flag-tagged TLR9 protein were expressed in HEK293T cells (left). Whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag Ab and immunoblotted with anti-cMyc Ab. (B) Quantification of binding activity was assessed by the ratio of IP-GzmA (white and red arrows) (lower left): the ratio of input GzmA (black arrow) was calculated from that of full-length GzmA (mean ± SEM, n = 4). *p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA test with Tukey's post-hoc test). (C) 3D structural model of mouse GzmA dimer (upper panel) generated using SWISS-MODEL Repository with its surface representation in the same view (lower panel) (72, 73). GzmA monomers are colored by exon (exon2, blue; exon 3, cyan; exon 4, yellow; exon 4, red). The Cys104-Cys104 disulfide bond between monomers is shown by spheres. This figure was created with the program PyMOL. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation western blot (WB) assay for the interaction between GzmA and TLR9 in primary FL-DCs. Whole-cell lysates were harvested 8 h after culture in the absence (1) or presence (2) of GzmA. These were immunoprecipitated using anti-TLR9 and immunoblotted with anti-TLR9 or anti-GzmA Ab. Results are representative of three independent experiments.