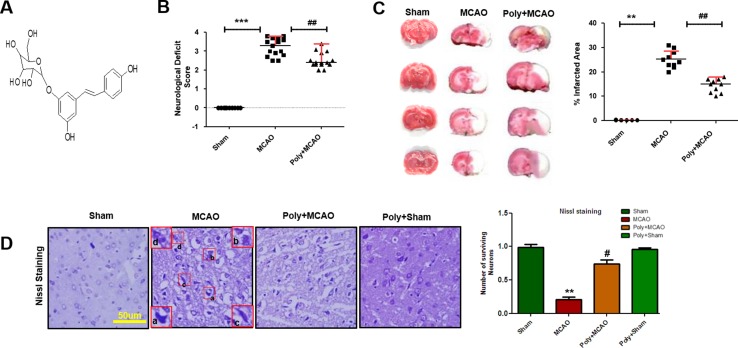
Figure 1.
Effect of polydatin on neurological scores, brain infarction and neurodegeneration. (A) Structure of polydatin. (B) Polydatin attenuated neurological deficits. Neurological test was conducted 24 h after ischemia. Poly+MCAO rats had significantly improvement of neurological deficits (## p < 0.01) compared to MCAO group. (C) Brain coronal sections were stained with TTC, which distinguishes between ischemic and non-ischemic areas (n = 5–10/group). (D) Representative photomicrograph of cresyl violet staining showing the extent of surviving neurons in the cortex, scale bar = 50 μm. (a, b) Cytoplasmic swelling and scalloped neurons with intense cytoplasmic eosinophilia and nuclear basophilia. These changes result from neuronal ischemia, which impairs metabolism in the tissue. (c) Cytoplasmic fading of neurons, which invariably occurs in neurons at later stages of necrosis (ghost neurons). (d) Some cells had shrunken appearance along with pyknotic nuclei. Intensive neuropil vacuolation can be seen in ischemic cortex (MCAO). ***p < 0.001; **, ## p < 0.01; # p < 0.05.