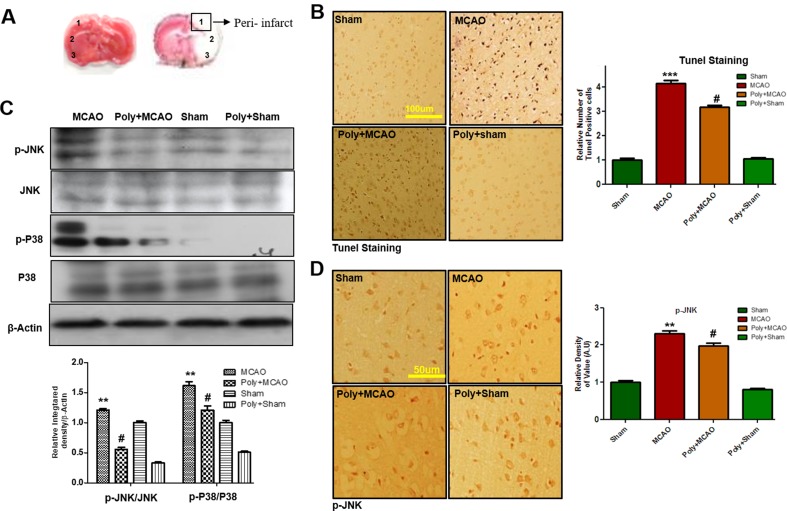
Figure 2.
Effect of polydatin on neuronal apoptosis and MAP kinase pathways. (A) TTC staining of coronal sections 24 h after permanent MCAO, separated by frontal cortex (1), parietal cortex and insular cortex (2), and periform cortex (3). The analyzed peri-infarct region, region of interest indicated by square 1 (B) Representative images of TUNEL histochemistry show apoptotic cells; scale bar = 100 μm. MCAO caused significant neuronal apoptosis, while polydatin treatment attenuated apoptotic damage. Data presented are relative to Sham (n = 3–5/group). (C) Polydatin prevents MCAO-induced activation of p-p38 and p-JNK. Representative Western blots of p-p38 and p-JNK (n = 5–8/group) and β-actin was used as a control. (D) Immunoreactivity of p-JNK; scale bar = 50 μm. p-JNK exhibits cytoplasmic localization, and number of experiment performed = 3. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; # p < 0.05.