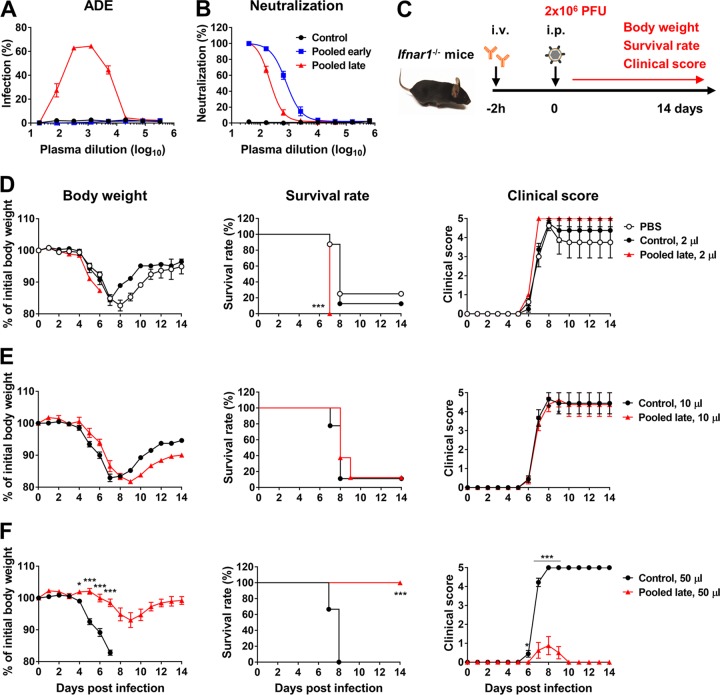
FIG 6.
In a lethal infection model, ZIKV-immune plasma samples mediate both ADE of infection and protection depending on infused amount. (A) ADE assays were performed as described for Fig. 1A with ZIKV-immune plasma samples (HU0015) pooled for those collected on day 21 (d21) pos or earlier (pooled early) or for those collected on day 28 pos or later (pooled late). (B) Neutralization assays were performed as described for Fig. 1A. In panels A and B, averages ± SD of results from three independent experiments are shown. (C) A schematic representation of an in vivo ADE assay in a lethal infection model. i.v., intravenous; i.p., intraperitoneal. (D) Ifnar1−/− mice (n = 8 per group) were intravenously administered 2 μl of PBS control (Hu0002) or pooled late plasma samples. At 2 h later, mice were intraperitoneally infected with 2 × 106 PFU of ZIKV (PRVABC59) and were monitored daily for body weight, survival, and clinical score as described in Materials and Methods. (E and F) Infection experiments were performed similarly to those described for panel D except that mice were treated with 10 μl (E) or 50 μl (F) of control or pooled late plasma samples. Data shown in panels D to F are presented as means ± SEM. Significant differences between groups with respect to body weight and clinical score were analyzed by multiple t tests using the Holm-Sidak method, and survival data were analyzed by log rank (Mantel-Cox) test. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.