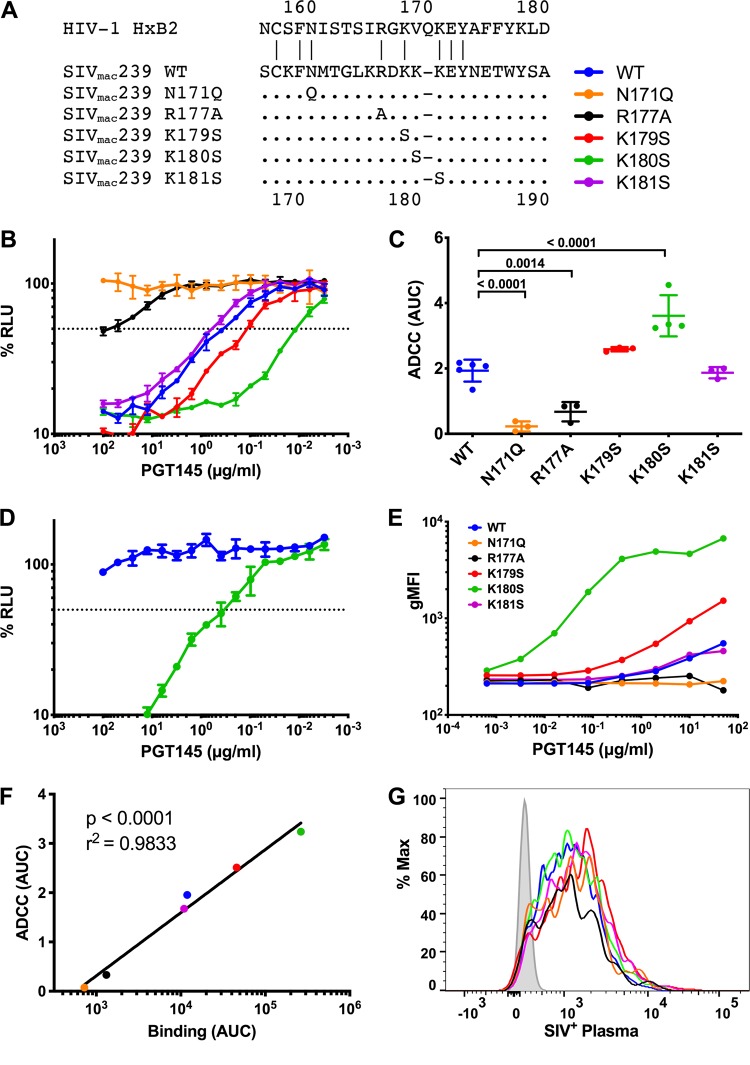
FIG 5.
PGT145 binds to the V2 apex of SIVmac239 Env. (A) Amino acid substitutions were introduced in the V2 region of SIVmac239 Env. The amino acid sequence of HIV-1HXB2 is shown for reference, and the positions indicated in the legend correspond to SIVmac239 Env. Dots indicate identity, and dashes indicate gaps. (B) CEM.NKR-CCR5-sLTR-Luc cells were infected with SIVmac239 carrying the indicated Env mutations and incubated with an NK cell line expressing human CD16 in the presence of serial dilutions of PGT145. ADCC activity was measured as the dose-dependent loss of luciferase activity in % RLU. The dotted line represents half-maximal lysis of infected cells, and the error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean from triplicate wells. (C) Area-under-the-curve (AUC) values for ADCC were calculated and compared by one-way ANOVA with a Holm-Sidak adjustment for multiple comparisons. (D) Wild-type SIVmac239 and SIVmac239 K180S were incubated with serial dilutions of PGT145 for an hour before infecting C8166-SEAP cells. Neutralization was determined by calculating the loss of secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) activity. The dotted line indicates 50% neutralization, and the error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean from triplicate wells. (E to G) CEM.NKR-CCR5-sLTR-Luc cells were infected with SIVmac239 V2 variants and stained with either PGT145 (E) or plasma from an SIVmac239-infected rhesus macaque (G). Fluorescence intensities are shown for viable infected (Gag+ CD4low) cells. PGT145 staining (AUC) was compared to ADCC (AUC) by Pearson correlation (F).