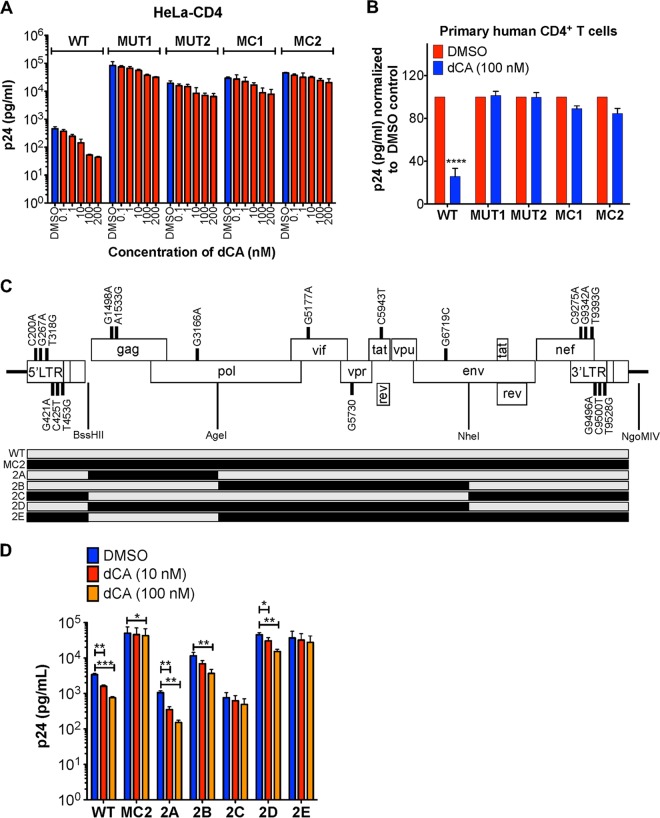
FIG 5.
Molecular clones mimic the dCA resistance of natural isolates. (A) HeLa-CD4 were infected with WT, MUT1, or MUT2 virus or with the molecular clones (MCs) of dCA-resistant viruses (MC1 or MC2). Cells were than washed and treated with the indicated concentrations of dCA or DMSO. Capsid p24 was measured 48 h posttreatment using p24 ELISA (n = 2). (B) MCs and viral isolates are resistant to dCA in primary human CD4+ T cells isolated from three donors. CD4+ T cells were infected and treated with DMSO or 100 nM dCA. Capsid p24 was measured by ELISA 6 days after treatment. Data are normalized to the values for 100% DMSO control for each virus. See Fig. S4 for raw data (n = 3). (C) MC2 chimeras and resistance to dCA. Schematics of recombinant MC2 chimeras. (Top) Molecular chimeras were made based on MC2, and mutations and restriction enzyme sites are indicated. (Bottom) Schematic of the recombinant chimeras 2A to 2E made from MC2. The gray and black segments indicate the sequences from WT and MC2, respectively. (D) Susceptibility to dCA of the constructed chimeras. Chimeras 2C and 2E with mutations in Nef/LTR (as well as Vif, Vpr, Tat, and Env for 2E) are highly resistant to dCA. HeLa-CD4 cells were infected with the indicated viruses before adding dCA. Viral capsid production in the supernatant was measured 48 h later by p24 ELISA. All data are presented as means plus SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post-test were used for statistical comparisons in panel D. Statistical significance: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.