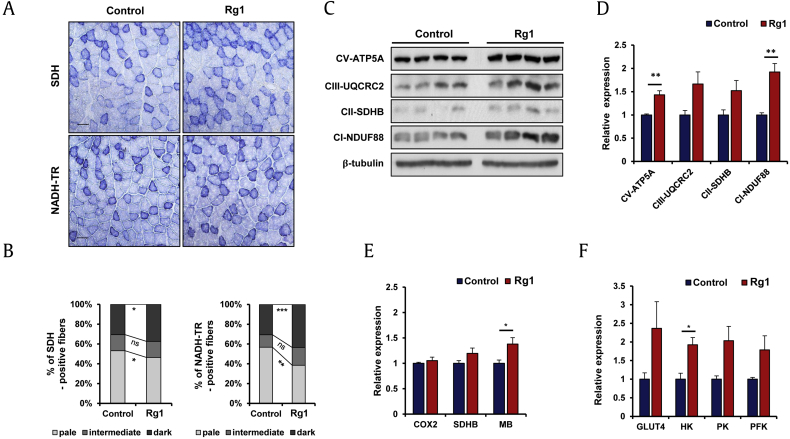
Fig. 3.
Rg1 promotes the metabolic function of mitochondria in skeletal muscle. (A) Succinic dehydrogenase (SDH) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase tetrazolium (NADH-TR) enzymatic activity in control- and Rg1-treated tibialis anterior (TA) muscles. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) The quantification of stained myofibers by three different staining grades (n = 3). The data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of respiratory chain components (CI–CV) from control- and Rg1-treated gastrocnemius (GAS) muscles. (D) The intensity of respiratory chain components (CI–CV) was normalized β-tubulin. The value of control-fed states were set to 1.0 (n = 4). The data represent the mean ± SD. **p < 0.01. (E, F) Real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis of mitochondrial and glycolytic genes in control- and Rg1-treated gastrocnemius (GAS) muscles (n = 4). The data represent thee mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05.
COX2, cyclooxygenase 2; GLUT4, glucose transporter type 4; HK, hexokinase; MB, myoglobin; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PFK, phosphofructokinase; PK, pyruvate kinase; SD, standard deviation; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; SDHB, SDH complex iron sulfur subunit B; SEM, standard error of mean.