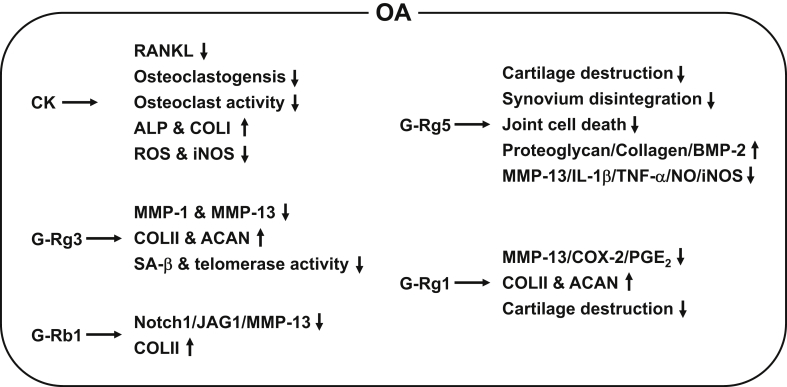
Fig. 3.
Schematic summary of the ameliorative effects of ginsenosides on OA pathogenesis. CK, G-Rg1, G-Rg3, G-Rg5, and G-Rb1 ameliorate OA by decreasing RANKL, ROS, NO, iNOS, MMP-1, MMP-13, Notch1/JAG1, SA-β, IL-1β, TNF-α, COX-2, PGE2, osteoclastogenesis, osteoclast activity, telomerase activity, cartilage destruction, synovium disintegration, and joint cell death, by increasing expression of ALP, collagens, ACAN, proteoglycan, and BMP-2, and by improving OA clinical symptoms in cells and animal models. ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ACAN, aggrecan; BMP-2, bone morphogenetic protein 2; CK, compound K; COLI, type I collagen; COLII, type 2 collagen; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; JAG1, jagged 1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; NO, nitric oxide; OA, osteoarthritis; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; RANKL, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SA-β, senescence-associated β; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.