Figure 5.
RARγ Required for DNA Damage-Induced Necroptosis in Keratinocytes and Promotes Carcinogen-Induced Papilloma
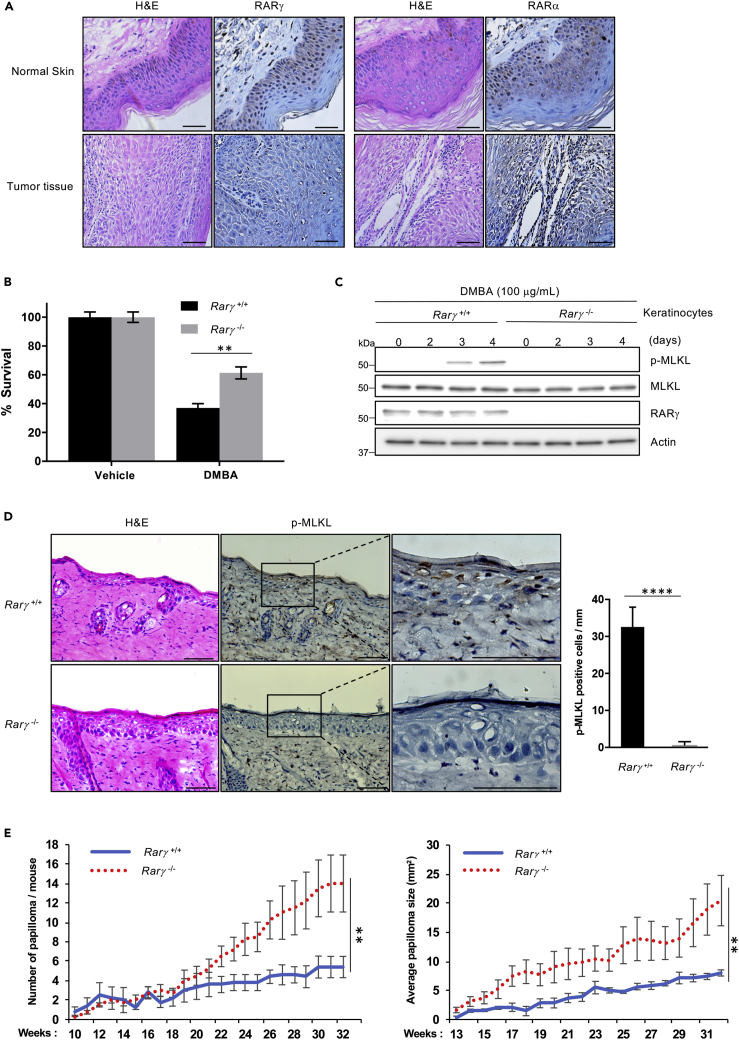
(A) Immunostaining of paraffin-embedded human SCC tumors and adjacent normal skin sections from human biopsy samples. Sections were stained with H&E or immunohistochemically stained with anti-RARγ or anti-RARα antibodies.
(B) Primary keratinocytes from Rarγ 1+/+ and Rarγ 1−/− mice were treated with DMBA or vehicle (acetone) for 5 days. Popidium iodide-positive population of cells mentioned above was determined by flow cytometry.
(C) Primary keratinocytes from RARγ1+/+ and RARγ1−/− mice were treated with DMBA or acetone for the indicated time. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting as indicated.
(D) Rarγ 1+/+ and Rarγ1−/− mice were treated with a single topical application of DMBA for 24 h, and the skin was collected. Skin sections were stained with H&E or immunohistochemically stained with anti-p-MLKL antibody. Right panel, the p-MLKL-positive cells were counted for 1 mm linear length of the epidermis.
(E) Rarγ1+/+ and Rarγ 1−/− mice were treated with a single topical application of DMBA followed 2 weeks later by twice weekly topical applications of TPA for 33 weeks. The number and size of papillomas on each mouse were recorded every 1 week. The average number of papillomas (more than 2 mm in diameter) per mouse is plotted versus the number of weeks post-initiation (left panel). Average papilloma size (in mm) was recorded for Rarγ1+/+ and Rarγ1−/− mice (right panel). See also Figure S6.
All blots and images above are representative of one of three experiments. Scale bar, 50 μm. Results shown in graphs are averages ± SEM from three independent experiments. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.