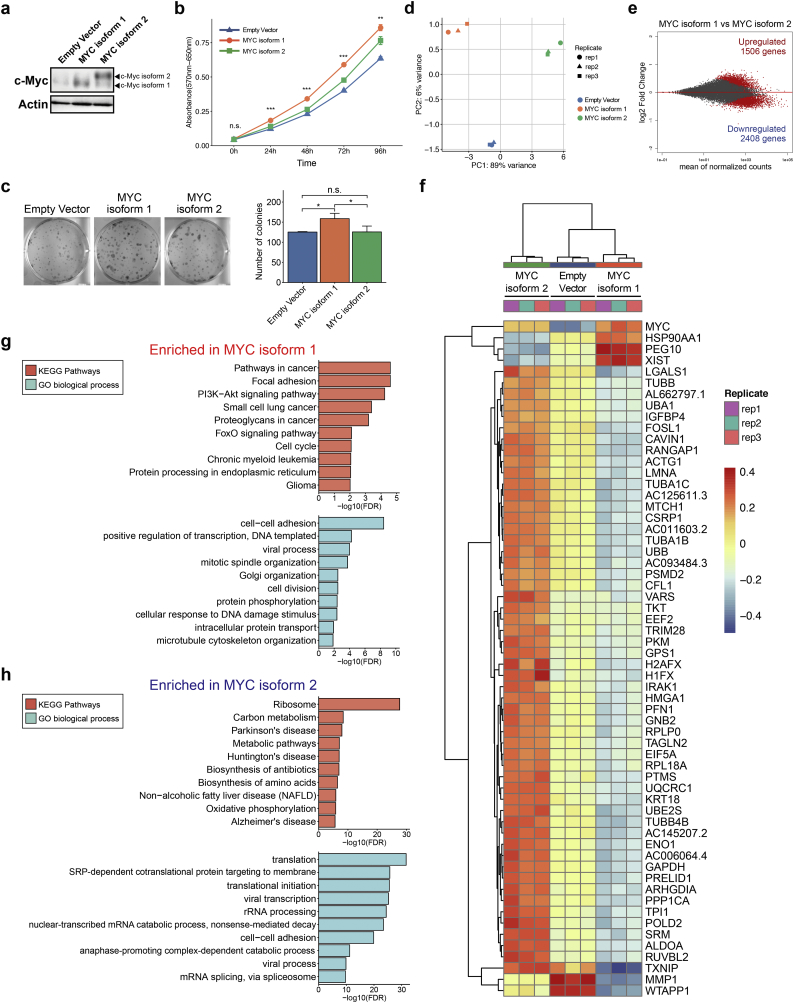
Fig. 5.
The differential effect of AUG- and CUG-initiated c-Myc isoforms (isoforms 1 and 2) against phenotypes and transcriptome.
(a) Western blot of c-Myc in the indicated KMST-6 stable cell lines. Actin was used as a loading control. c-Myc isoforms 1 and 2 are indicated by arrowheads.
(b) Proliferation curve of the indicated KMST-6 stable cell lines measured by MTT assays.
(c) Representative images (left) and quantification of the colonies (right) of the indicated KMST-6 stable cell lines at day 14.
(d) Principal component analysis of the indicated KMST-6 stable cell lines. Genes with zero counts across all samples were excluded from the analysis.
(e) MA-plot of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the indicated KMST-6 stable cell lines. DEGs are represented as red dots. The cutoff of DEGs was determined as FDR < 0.01 (likelihood ratio test). The numbers of significantly up- or downregulated genes are shown.
(f) Hierarchical clustering of the top 60 DEGs (FDR < 0.01, likelihood ratio test) among the indicated KMST-6 stable cell lines. Regularized log2 expression values are row-mean subtracted.
(g,h) Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of significantly upregulated genes in c-Myc isoform 1 (g) and isoform 2 (h). Top 10 significantly enriched KEGG pathways and GO biological process are shown (FDR < 0.05).
Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. n.s., not significant; (*) p < 0.05; (**) p < 0.01; (***) p < 0.001. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)