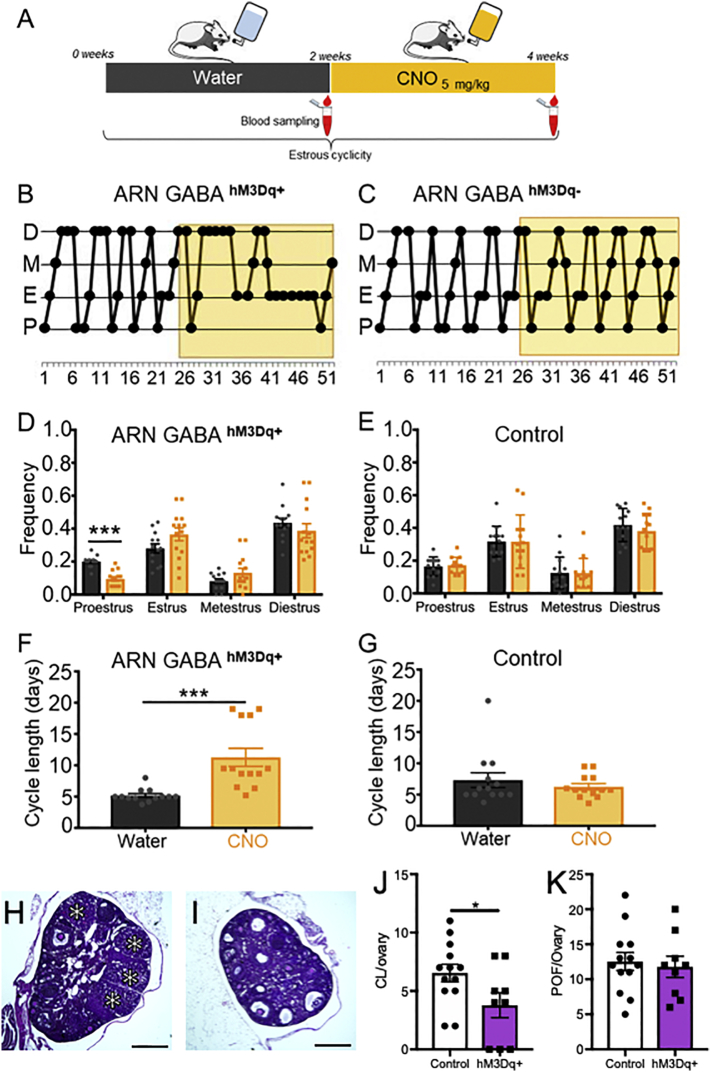
Fig. 6.
Chronic exposure to CNO activation of ARN GABA neurons disrupts estrus cyclicity in female mice. (A) Schematic of the protocol to chronically activate hM3Dq-expressing ARN GABA neurons with CNO administration through the drinking water. (B,C) Representative examples of estrous cyclicity before and during CNO (yellow box) exposure in an ARN GABAhM3Dq+ female and in a ARN GABAOFF Target control animal. (D,E) Mean ± SEM frequency of each estrous cycle phase before (water; grey bars) and during CNO exposure (CNO; yellow bars) in ARN GABAhM3Dq+ females (N = 13) and in control animals (N = 13, consisting of ARN GABAOFF Target and ARN GABAmCherry female mice). (F,G) Mean ± SEM cycle length in days before and during CNO exposure. (H—K) Representative images of ARN GABAmCherry (H) and ARN GABAhM3Dq+ (I) ovarian histology; corpora lutea marked with asterisks (*). Mean ± SEM number of preovulatory follicles (POF; J) and corpora lutea (CL; K) from control (ARN GABAmCherry and ARN GABAOFFTarget; N = 13) and ARN GABAhM3Dq+ (N = 9) mice following CNO administration. * p < .05; ***p < .001; (D,E) Multiple Student's t-tests; (F,G) Mann-Whitney U test; (J,K) Student's t-tests. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)