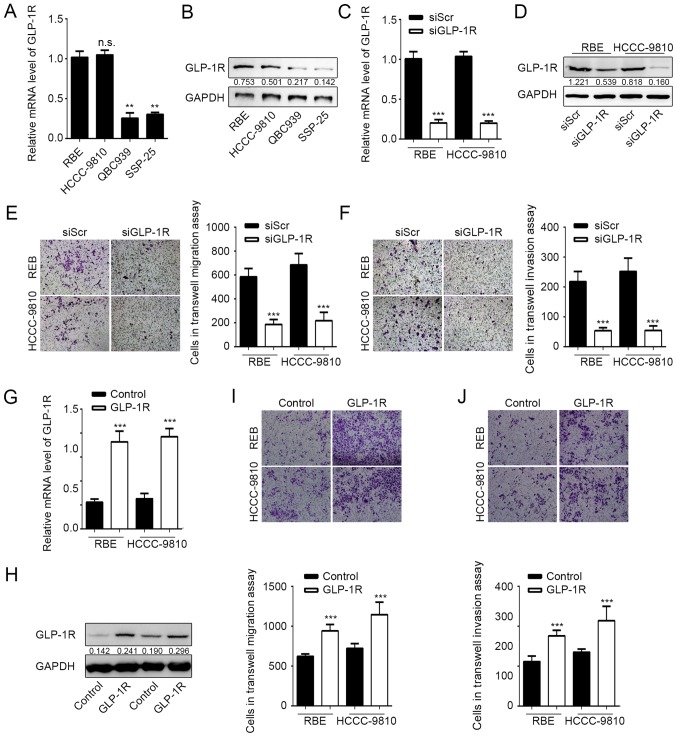
Figure 1.
Knockdown of GLP-1R inhibits intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell migration and invasion. (A) GLP-1R mRNA expression levels in different cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. **P<0.01 vs. RBE. (B) GLP-1R protein expression levels in different cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Knockdown of GLP-1R in RBE and HCCC-9810 cells was confirmed by (C) western blot analysis and (D) reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. ***P<0.01 vs. SiScr. Transwell assays were used to determine the effects of GLP-1R silencing on the (E) migration and (F) invasion of RBE and HCCC-9810 cells. ***P<0.001 vs. siScr. Overexpression of GLP-1R was confirmed by (G) reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and (H) western blot analysis. ***P<0.001 vs. Control. Transwell assays were used to determine the effect of GLP-1R overexpression on the (I) migration and (J) invasion of RBE and HCCC-9810 cells. ***P<0.001 vs. Control. n.s., not significant; GLP-1R; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; si, small interfering RNA. Representative images for Transwell assays were obtained using ×20 magnification. n.s., not significant.