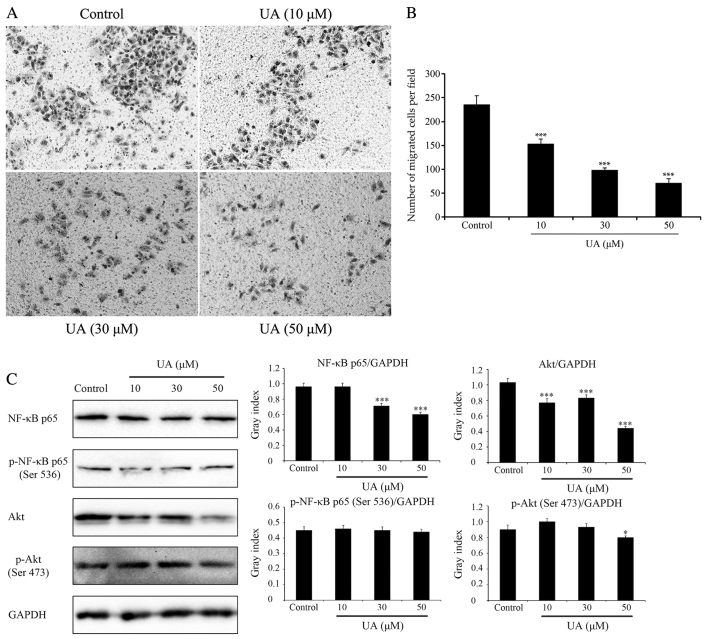
Figure 2.
Effects of UA on cell migration and signaling pathways (NF-κB and Akt). Effects of UA on GBC-SD cell migration, evaluated using a Transwell assay. Cells suspended in serum-free RPMI-1640 were overlaid in the upper chamber of each Transwell. Following incubation with different concentrations of UA for 24 h, penetrating cells were stained with crystal violet and recorded under a microscope mounted with a CCD camera. (A) Images depicting migration of GBC-SD cells. (B) Quantified data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. ***P<0.001, vs. control group (0 µM). (C) Effect of UA treatment on the NF-κB and Akt signaling pathways. In GBC-SD cells treated with various UA concentrations for 6 h, expression of NF-κB p65, p-NF-κB p65 (Ser536), Akt and p-Akt (Ser473) was analysed by western blotting. GAPDH was used as the sample loading control. Quantification of protein bands densitometry was carried out using ImageJ software. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001, vs. control group (0 µM). UA, ursolic acid; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; Akt, protein kinase B; p-, phosphorylated.