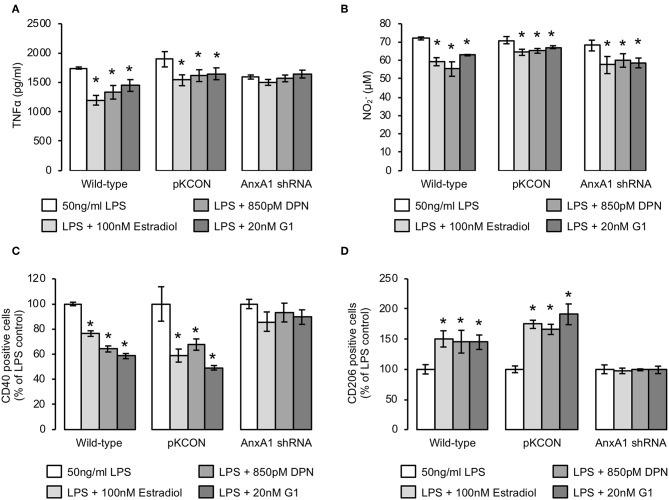
Figure 5.
The anti-inflammatory effects of estrogen are largely dependent upon AnxA1 expression. (A) Stable transfection of BV2 cells with an shRNA sequence targeting AnxA1, but not with an empty plasmid control (pKCON), inhibits the ability of estradiol, DPN or G1 (16 h) to suppress LPS-induced TNFα production (2 h pre-treatment); data are means ± sem, n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. LPS-treated control cells. (B) Neither stable transfection of BV2 cells with an empty plasmid control (pKCON) nor with an shRNA sequence targeting AnxA1 affects the ability of estradiol, DPN or G1 (16 h) to suppress LPS-induced nitrite production (2 h pre-treatment); data are means ± sem, n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. LPS-treated control cells. (C) Stable transfection of BV2 cells with an shRNA sequence targeting AnxA1, but not with an empty plasmid control (pKCON), inhibits the ability of estradiol, DPN or G1 (16 h) to suppress LPS-induced surface expression of the pro-inflammatory marker CD40 (2 h pre-treatment); data are means ± sem, n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. LPS-treated control cells. (D) Stable transfection of BV2 cells with an shRNA sequence targeting AnxA1, but not with an empty plasmid control (pKCON), inhibits the ability of estradiol, DPN or G1 (16 h) to reverse LPS-suppressed expression of the anti-inflammatory marker CD206 (2 h pre-treatment); data are means ± sem, n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. LPS-treated control cells.