Figure 6.
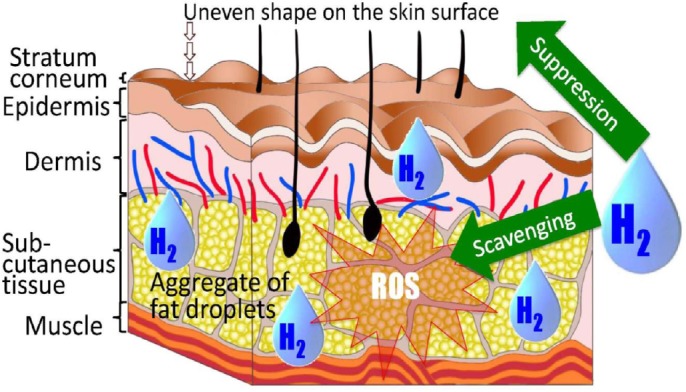
Mechanism assumed for cellulite formation and its hydrogen (H2)-attributed suppression.
Note: Cellulite is presumed to be formed by (1) abnormally excessive accumulation of lipid droplets in adipocytes, (2) adipocyte cell death resulting from loading of oxidative stress to lipid droplets, (3) excessive oxidation of extracellular fat preceded by release of intracellular fat into the extracellular space, and (4) protrusion of the skin surface due to deterioration or solidification of fat. Cellulite formation is considered to be suppressed by the inhibitory effect of hydrogen on the formation of lipid droplets, oxidative stress, and excessive oxidation. ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
