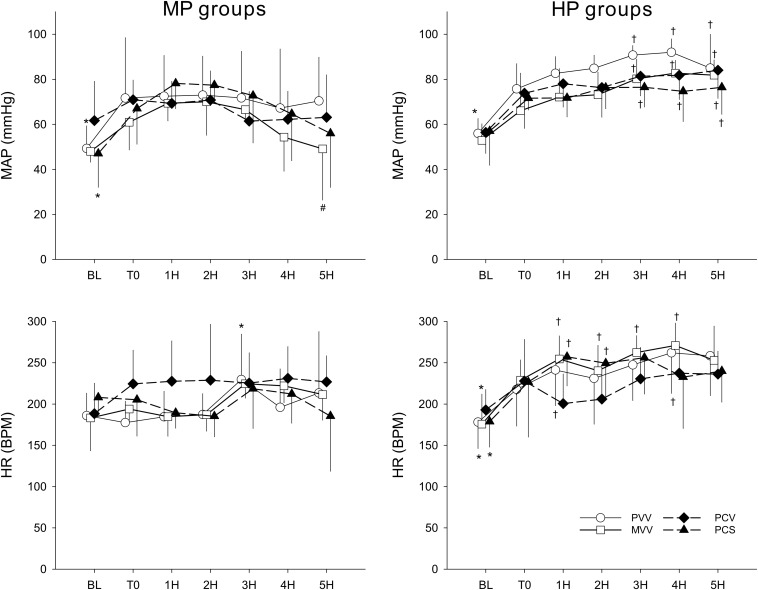
FIGURE 4.
Changes in haemodynamic parameters before (BL), after the induction of lung injury (T0), and during the application of various ventilation modes. Left panels display changes in groups ventilated with a PEEP of 6 cmH2O, whereas groups depicted in the right panels were ventilated with a PEEP of 9 cmH2O. Data are presented as group means ± half-width of 95% confidence interval. MP, moderate PEEP. HP, high PEEP. MAP, mean arterial pressure. HR, heart rate. BPM, beats per minute. 1H–5H, averages of measured parameters during the corresponding 1 h period of ventilation with an experimental pattern. PVV, physiological variable ventilation. MVV, mathematical variable ventilation. PCV, pressure-controlled ventilation. PCS, pressure-controlled ventilation with regular sighs. Results of the ANOVA analyses (p-values) for factor “ventilation mode.” p < 0.01 for MAP and p = 0.79 for HR; for factor “PEEP”: p < 0.01 for all variables; for the interaction of “ventilation mode * PEEP”: p = 0.24 for MAP, p < 0.01 for HR; for interaction of “ventilation mode * PEEP * time”: p < 0.01 for all variables. *p < 0.05 vs. T0. #p < 0.05 vs. PVV. †p < 0.05 vs. MP.