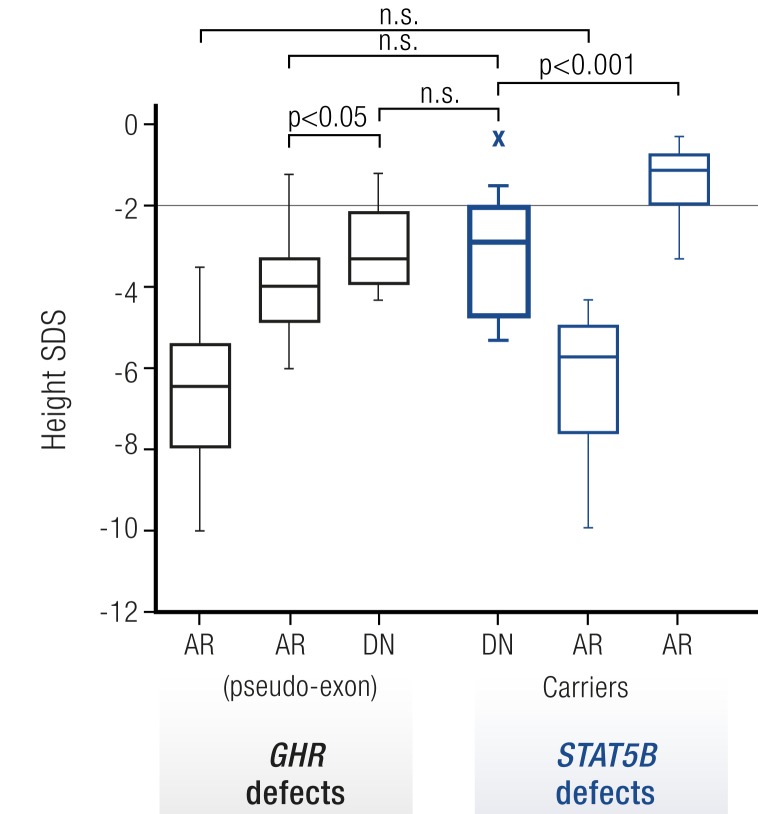
Figure 4.
Heights of dominant negative STAT5B patients are comparable to dominant negative GHR patients. Height SDS values of GHIS patients with GHR mutations (black) were compared with height SDS values of STAT5B mutational carriers (blue). GHR defects: AR, autosomal recessive GHR mutations (n = 100); AR pseudoexon, GHR pseudoexon 6Ψ mutations (n = 21); DN, dominant negative GHR mutations (n = 16). STAT5B defects: DN, dominant negative STAT5B mutations (n = 11); AR, autosomal recessive STAT5B mutations (n = 10); AR carriers, STAT5B mutation carriers (n = 14). Box (median, 25th and 75th percentiles) and whiskers (minimum and maximum values) plots. Statistical analysis was by the Student t test. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. n.s., not significant (122). [Reproduced with permission from Klammt J, Neumann D, Gevers EF, et al. Dominant-negative STAT5B mutations cause growth hormone insensitivity with short stature and mild immune dysregulation. Nat Commun 2018;9:2105.]