FIGURE 1.
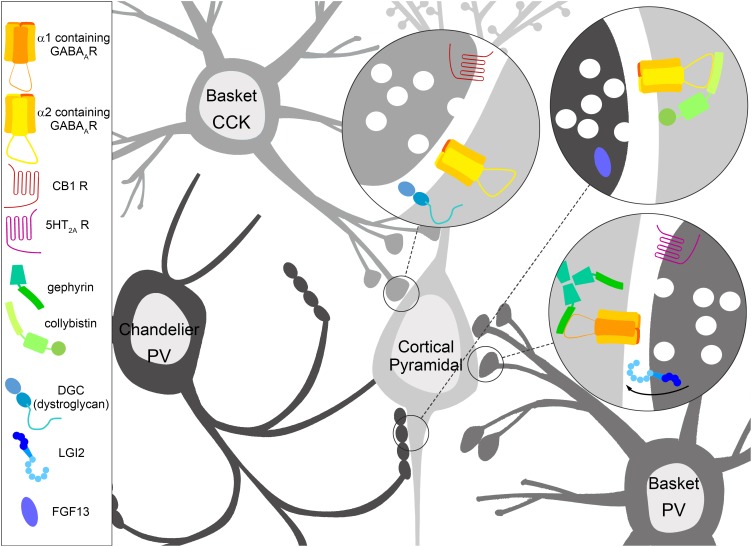
Specialization of inhibitory GABAergic synapse subtypes. Interneurons have molecular specifications which help guide, form, and maintain GABAergic synapses onto distinct areas of the cortical pyramidal cell, which in turn feature molecular specialization in terms of enriched GABAA receptor (GABAAR) subtypes and interacting proteins. Cholecystokinin (CCK) positive basket cells target the soma of pyramidal cells, where the dystrophin glycoprotein complex (DGC) containing dystroglycan and GABAARs containing the α2 subunit are robustly expressed. The CCK positive presynaptic terminal is enriched with Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1). Parvalbumin (PV) positive basket cells target the soma of pyramidal cells enriched with GABAARs containing the α1 subunit anchored by gephyrin. The PV positive presynaptic terminal contains the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor, which is thought to depolarize PV positive basket cells. LGI2 protein is enriched in PV positive basket cells during synaptogenesis, and regulates the formation of these synapses. PV positive chandelier cell cartridges target the axon initial segment (AIS) of pyramidal cells. GABAARs containing the α2 subunit are enriched here, and collybistin interaction plays a key role in AIS localization, although both collybistin and α2 are found at other inhibitory contact sites. The non-secreted protein FGF13 is enriched in PV positive chandelier cells during synaptogenesis, and regulates the formation and maintenance of these synapses.