Figure 6.
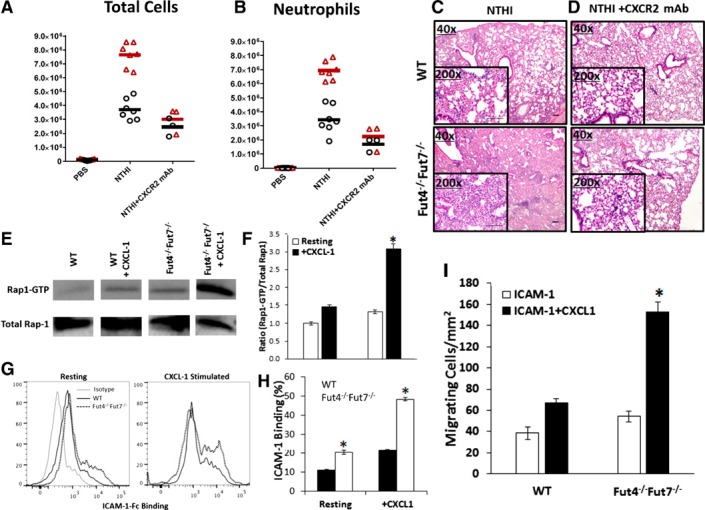
Blocking the CXCL‐1 CXCR2 axis normalizes and reduces recruitment to the lung by attenuating the excess Rap‐1 GTP signaling and ICAM‐1 binding in Fut‐deficient neutrophils. BALF was collected 18 h after instillation of NTHI and total cells (A), and neutrophil counts (B) were taken (n = 6 mice for each subgroup). *P < 0.05 vs. WT of each subgroup. ***P < 0.001 vs. WT of each subgroup. ‡ P < 0.01 vs. WT+NTHI sample. Images of lung sections of WT or Fut4−/−Fut7−/− animals treated with NTHI and no mAb (C) or anti‐CXCR2 (D). Magnification, ×40 and ×200 (inset). Scale bar, 100 μm. Representative immunoblots (E) and density blots (F) are shown for total Rap1 and Rap1‐GTP from murine neutrophils stimulated with PBS or recombinant CXCL1. Density plots were calculated using image‐analysis software. Data are presented as means ± sem. *P < 0.05 vs. WT ratio. (G, H) Percentage of resting or CXCL1 stimulated neutrophils binding to recombinant ICAM‐1 Fc. (I) Number of migrating neutrophils on ICAM‐1 and ICAM‐1+CXCL‐1 surfaces at a shear flow rate of 800 s−1. *P < 0.05 vs. the no‐CXCL1 subtype.
