Figure 8.
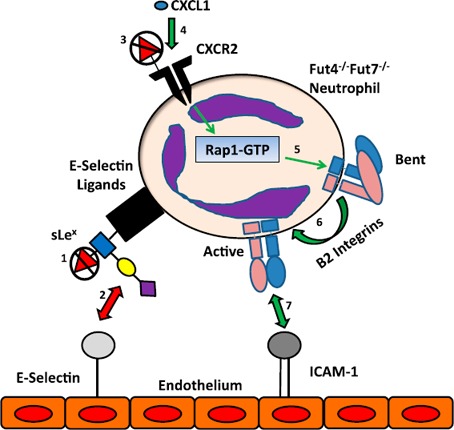
Altered binding pathways in Fut4−/−Fut7−/− neutrophils. The different binding mechanisms affected by the loss of α(1,3) fucose in Fut4−/−Fut7−/− deficient mice during recruitment of neutrophils to the acutely inflamed lungs. Previous studies have demonstrated that Fut4−/−Fut7−/− neutrophils have lost the fucose residue of sLeX (1) on their selectin ligands and therefore do not interact with endothelial bound E‐selectin (2). On the other hand, the loss of fucose on CXCR2 (3) leads to enhanced chemokine signaling (CXCL1 was tested but other cytokines can signal through CXCR2, as well) through the receptor (4), which in turn up‐regulates Rap1‐GTP (5). This process leads to more β2‐integrins in their high‐affinity state (6). More active β2‐integrins (LFA‐1/Mac‐1) lead to a greater interaction with ICAM‐1 on the endothelial surface and therefore more migration on the endothelium and emigration into the lung (7). Red arrows: interactions that are down‐regulated, whereas green arrows indicate those that are up‐regulated upon α(1,3) fucose deficiency.
