Figure 5.
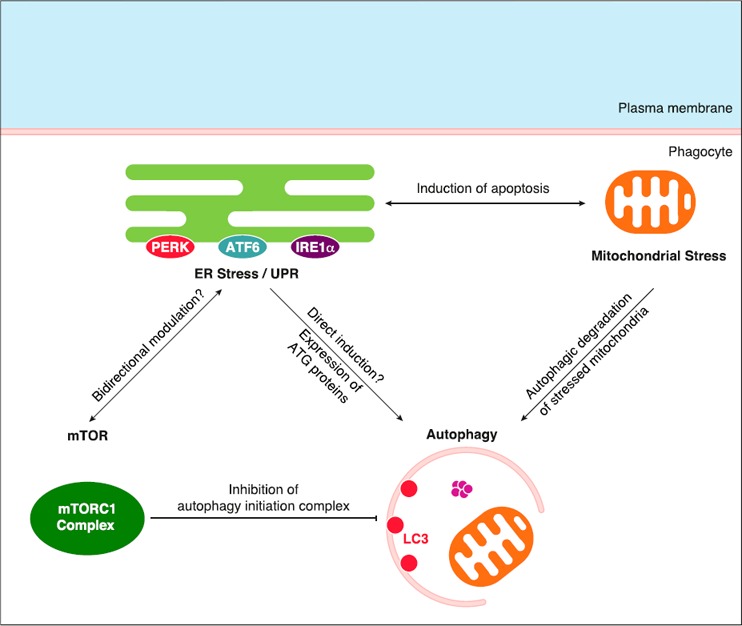
Connections between ER stress/UPR, mTORC1 pathway, autophagy, and mitochondrial stress. mTORC1 complex is known to inhibit autophagy via the inhibitory phosphorylation of components of the autophagy initiation complex. ER stress/UPR might promote autophagy directly or via expression of ATG proteins found among UPR target genes. Moreover, a bidirectional modulation seems to connect ER stress/UPR and the mTOR pathway, although no precise mechanism has been described. ER stress/UPR cooperates with mitochondrial stress (via Ca2+ flux and ROS production) to induce apoptosis. Stressed/damaged mitochondria are subjected to ubiquitination and recruitment to the autophagy machinery, which leads to their autophagic degradation.
