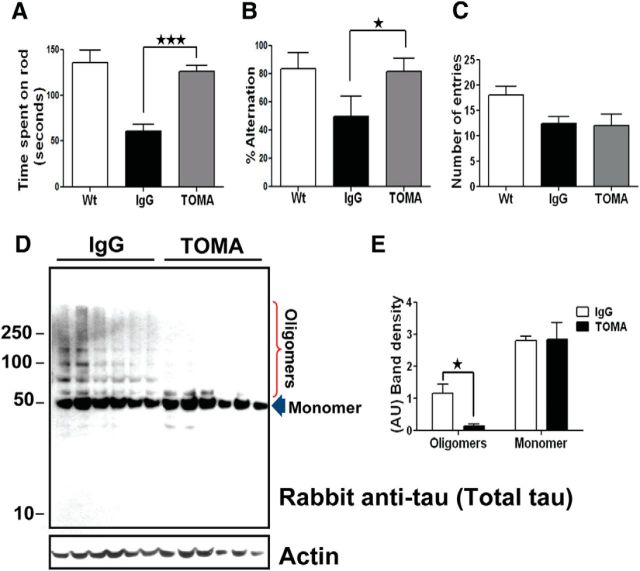
Figure 5.
A single intravenous injection of TOMA reverses phenotypes and clears tau oligomers in 8-month-old P301L mice. Three groups of mice (n = 10 /group): (1) Wt: wild-type mice that received saline injection, (2) Control IgG: P301L immunized with nonspecific IgG antibody (anti-rhodamine, 30 μg/animal), (3) TOMA: P301L immunized with TOMA (30 μg/animal). Animals were evaluated using the rotarod task for locomotor deficits and the Y-maze task for memory deficits. A, The rotarod test showed improvement of motor performance in mice immunized with TOMA (gray bar) compared with the control group (black bar). ★★★ p < 0.0003, one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc comparison. No statistically significant differences were found between the TOMA group and wild-type mice (white bar). B, The Y-maze memory test showed improved retention in TOMA-treated animals as depicted by the number of completed alternations in the Y-maze, defined as successive entry into each of the three arms of the maze without reentry into a previously visited arm. The differences were statistically significant. ★p < 0.02, one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc comparison. C, Total number of entries into all arms of the maze. D, Representative Western blot of PBS soluble fraction from brain homogenate of mice intravenous immunized with the nonspecific IgG antibody (lanes 1–6) and mice immunized with TOMA (lanes 7–12) detected with rabbit anti-tau antibody, which recognizes all tau aggregates. Internal control is shown at the bottom. E, Graphs represent the band intensity relative to rabbit anti-tau antibody (arbitrary units, AU). The differences were statistically significant. ★p < 0.005, two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc comparison. Bars represent means and error bars SEM.