Figure 2.
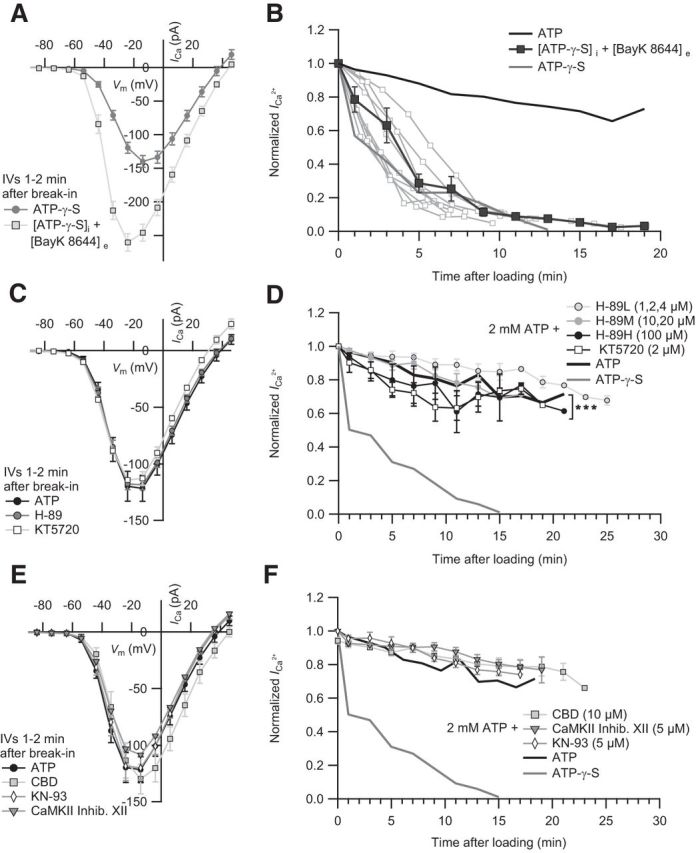
Probing the requirement of IHC ICa for phosphorylation by PKA and CaMKII. A, The IV of IHCs dialyzed with ATP-γ-S in the absence (n = 15) and presence of 5 μm extracellular BayK 8644 (n = 15). B, BayK 8644 did not significantly prevent the ICa rundown (p = 0.43, statistical comparison was performed between 1 min and 13 min after loading). Mean normalized ICa values of IHCs dialyzed with ATP-γ-S (n = 13) in the presence of BayK 8644 (n = 9). For comparison, we display the mean normalized ICa of IHCs dialyzed with ATP. C, The effect of PKA inhibition on IHC ICa. The IVs of IHCs dialyzed with ATP in the absence (n = 5) or presence of intracellular H-89 (n = 14) or KT5720 (n = 5) are comparable. D, The normalized mean ICa values of IHCs dialyzed with low (1, 2, and 4 μm, n = 6), middle (10 and 20 μm, n = 5), or high (100 μm, n = 3) concentration of H-89 or KT5720 (2 μm, n = 6) over time. Statistical comparison was performed between 3 min and 19 min after loading. E, CaMKII inhibition shows no effect on IHC ICa. The IVs of IHCs dialyzed with ATP in the absence (n = 5) or presence of intracellular CBD (n = 4), CaMKII Inhibitor XII (n = 3), or KN-93 (n = 4). F, The rundown of the mean normalized ICa in IHCs dialyzed with CBD (n = 4), inhibitor XII (n = 4), and KN-93 (n = 3) is similar to controls. In comparison, the mean normalized ICa of IHCs dialyzed with ATP or ATP-γ-S is displayed. ***p < 0.001.
