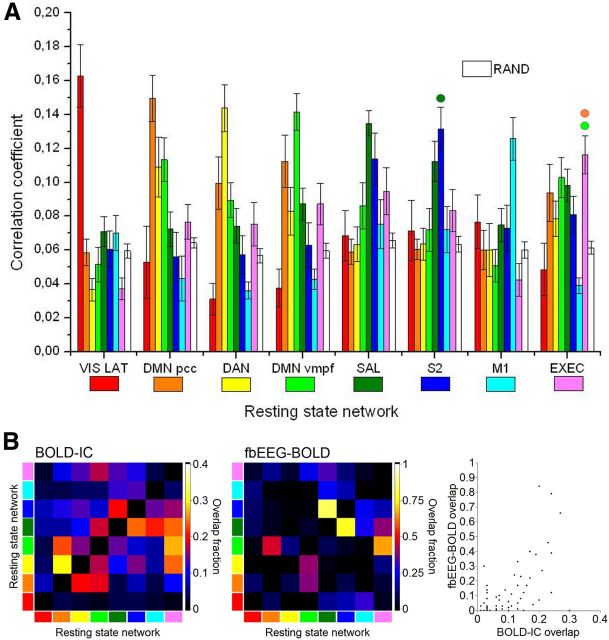
Figure 3.
Spatial correlations between fbEEG—fMRIbin maps and BOLD_RSNbin maps are specific to the corresponding BOLD IC for most RSNs and greater than in randomized data. A, Mean correlation coefficients between fbEEG–fMRIbin maps and BOLD_RSNbin maps (error bars indicate SEM). In paired statistical comparisons, for each network between the correlation value for the best-fitting map compared with the other seven, all other differences are significant at p < 0.05 (Holm–Bonferroni corrected) except for DMNvmpf-EXEC, DMNpcc-EXEC, and SAL-S2 (marked with colored circles). Maps are organized in descending order of averaged correlation coefficients. B, Spatial overlap between BOLD_RSNbin (left) and fbEEG-fMRIbin (middle) maps was quantified with a correlation coefficient.