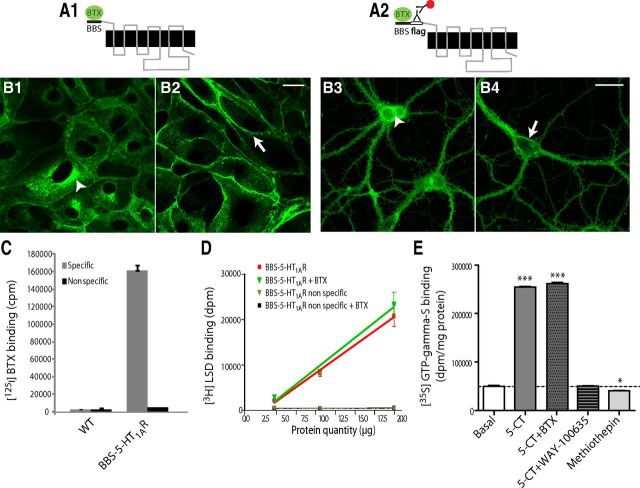
Figure 1.
BBS-5-HT1AR and BBS-Flag-5-HT1AR constructs: expression, pharmacology, and coupling. A, Schematic illustration of the folding of the membrane-integrated BBS-5-HT1AR and BBS-Flag-5-HT1A. The minimum site for BTX recognition site, BBS, is alone (A1) or combined with a Flag tag (A2) genetically fused to the N-terminus domain of 5-HT1AR. BBS binds BTX and tag Flag is recognized by an anti-Flag antibody that can be labeled by a fluorescent secondary antibody (antibody complex). B, Confocal microscopy images of BBS-5-HT1AR and BBS-Flag-5-HT1A stained by (1) BTX-AF488 in permeabilized (B1, arrowhead; endoplasmic reticulum labeling) or intact-transfected (B2, arrow; plasma membrane labeling) LLC-PK1 cells or (2) antibody complex in transduced permeabilized (B3, arrowhead; endoplasmic reticulum labeling) or intact (B4, arrow; plasma membrane labeling) neurons in primary culture from E18 hippocampus. Scale bars: 20 μm. C, Specific [125I]BTX binding to LLC-PK1 cells transfected or not (WT) with BBS-5-HT1AR. Nonspecific binding was quantified with [125I]BTX (1 nm) plus unlabeled BTX (100 nm). D, [3H]LSD binding without or with BTX (100 μm) onto membranes from BBS-5-HT1AR-transfected LLC-PK1 cells. Nonspecific binding was determined with [3H]LSD plus 10 μm 5-HT. E, Effects of 5-CT (1 μm), alone or with BTX (100 μm) or WAY-100635 (1 μm), and methiothepin (1 μm) on [35S]GTPγS binding to membranes from BBS-5-HT1AR-transfected LLC-PK1 cells. One-way ANOVA, Dunnett's test, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.