Figure 6.
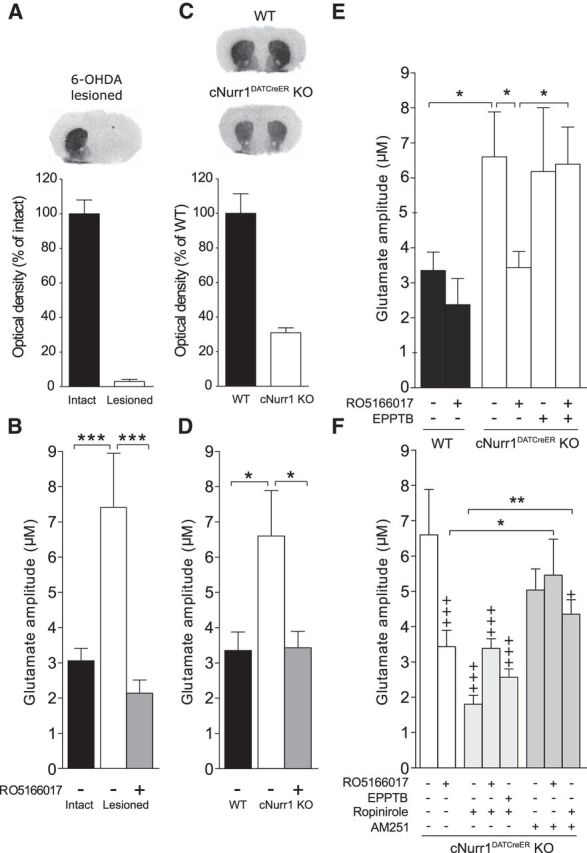
DAT levels and striatal glutamate release under dopamine deficiency and the modulatory effects of TAAR1, ropinirole, and AM251. A, Autoradiographic detection of DAT by [125I]RTI-55 in brain slices revealed a 97 ± 1.3% reduction in the lesioned compared with the intact hemisphere of MFB 6-OHDA-treated C57BL/6J mice (n = 10). B, Real-time in vivo amperometry revealed significantly enhanced glutamate release in the lesioned hemisphere compared with the intact hemisphere. This hyperglutamatergic state was reversed after local application of the TAAR1 agonist RO5155017. C, There was a 67 ± 3.8% reduction in DAT levels in cNurr1DATCreER KO (n = 6) compared with WT mice (n = 6). D, KCl-evoked glutamate concentrations were significantly enhanced in the striatum of KO mice compared with WT mice. This effect was normalized after local application of RO5166017. E, Local administration of EPPTB did not significantly affect KCl-evoked striatal glutamate release in cNurr1DATCreER KO animals, but blocked the effect of RO5166017 when these compounds were coadministered. F, Local administration of ropinirole attenuated KCl-evoked glutamate amplitudes in striatum. Coadministration of ropinirole did not significantly change the effects of RO5166017 or EPPTB in cNurr1DATCreER KO animals. AM251 had no effects by itself, but attenuated the inhibitory effect of RO5166017 on KCl-evoked glutamate release. Likewise, AM251 attenuated the inhibitory effect of ropinirole. The WT vehicle, cNurr1DATCreER KO vehicle, and RO5166017 data have been included in several graphs to facilitate comparisons. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM from 4–5 glutamate peaks from 5–10 animals/treatment. DAT, Dopamine transporter;. +p < 0.05, +++p < 0.001 vs WT vehicle; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.01 vs indicated group by Fisher's LSD post hoc test.
