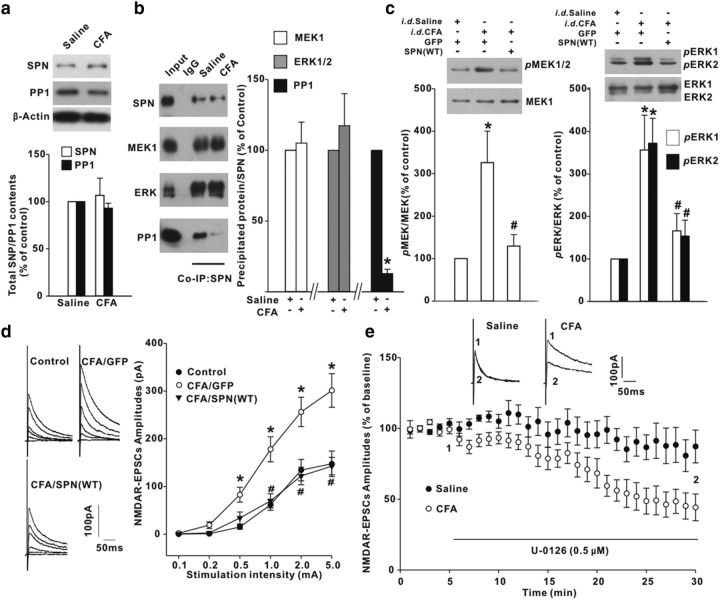
Figure 8.
Intraplantar injection [intradermal (i.d.)] of CFA reduced the inhibitory effects of SPN on MEK/ERK signaling in spinal dorsal horn of rats. a, CFA had no effects on total protein levels of SPN and PP1. n = 6 experiments. b, Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) was performed with anti-SPN antibody from synaptosomal fraction of spinal dorsal horn. The precipitates were immunoblotted with antibodies indicated on the left of panels. n = 6 experiments, *p < 0.05 relative to saline control. c, Effects of SPN(WT) on CFA-induced MEK/ERK phosphorylation. Intrathecal viral injection (i.t.) was performed at 2 h post-CFA and immunoblotting was conducted at day 3 post-CFA. n = 6 experiments. d, NMDAR EPSCs were elicited at six different stimulation intensities (left) and the input–output curves were plotted (right). n = 10 neurons in each group. *p < 0.05 relative to saline-injected GFP-expressing control rats. #p < 0.05 relative to CFA-injected GFP-expressing rats. e, Effects of U-0126 on NMDAR EPSCs recorded in slices from saline-injected or CFA-injected rats. The horizontal bar indicated the period of U-0126 perfusion. n = 6 neurons in each group.