Figure 2.
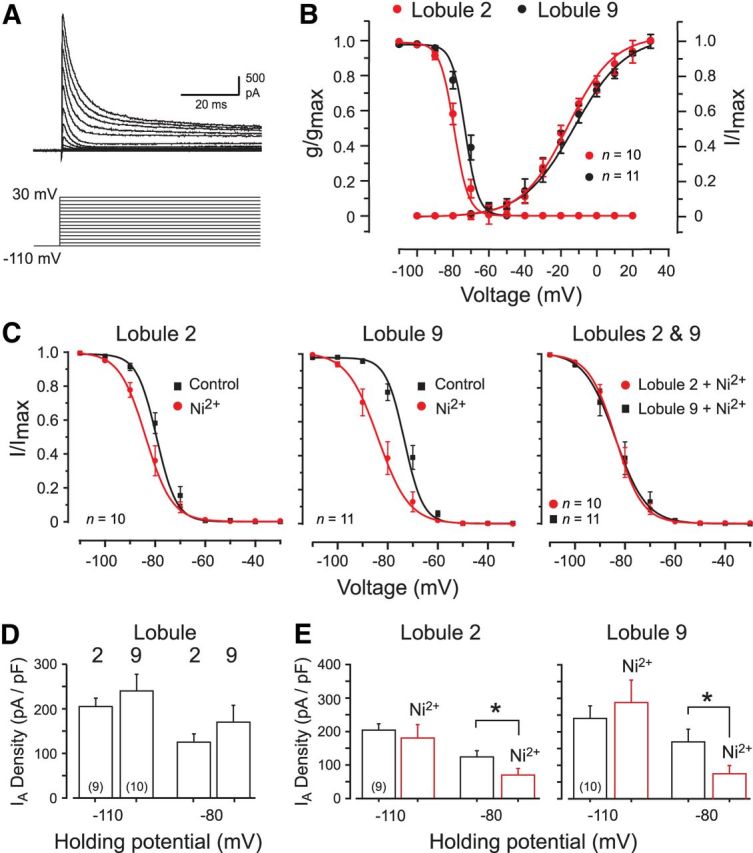
Biophysical properties of A-type current in granule cells of lobules 2 and 9. All recordings were conducted in the absence of calcium channel blockers unless indicated. A, Kv4 current (IA) evoked in a lobule 9 granule cell over the indicated potentials. B, Mean conductance and voltage-inactivation plots for IA in lobule 2 and 9 granule cells superimposed for comparison. C, Voltage-inactivation plots for IA in lobule 2 and 9 granule cells before and after 300 μm Ni2+ to block the Cav3–Kv4 interaction. Ni2+ produces a greater leftward shift of Vh in lobule 9 cells (left and middle), with a common Vh in either lobule once Cav3 current is blocked (right). D, Bar plots of IA density evoked by a step to −30 mV from two different holding potentials that are beyond (−110 mV) or within (−80 mV) the range of Ni2+-sensitive shifts in IA Vh. E, Bar plots of IA density evoked by a step to −30 mV from either −110 or −80 mV before and after 300 μm Ni2+. *p < 0.05 (Student's paired t test).
