Figure 7.
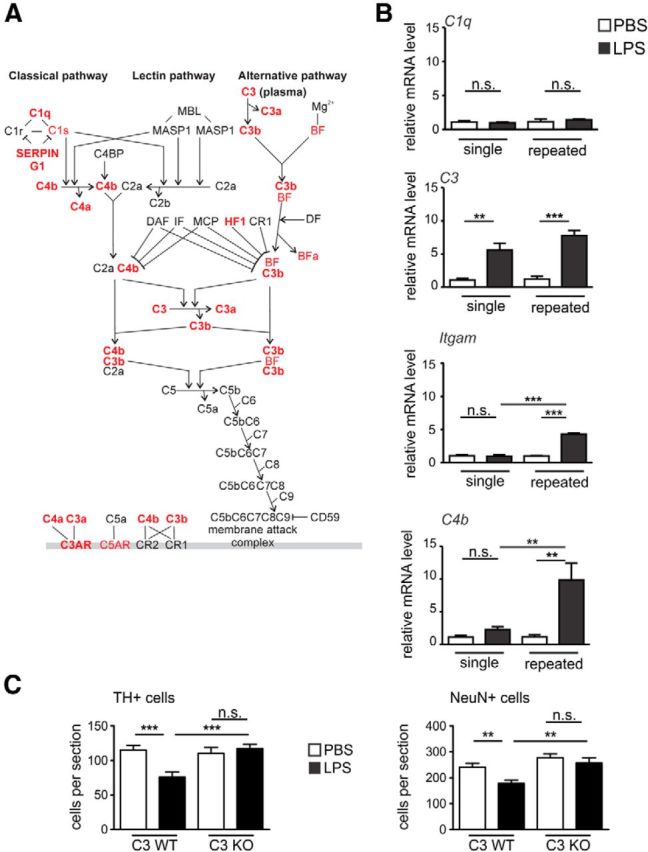
The complement pathway is activated and involved in neurodegeneration after repeated LPS application. A, The complement system canonical pathway of mice after single or repeated intraperitoneal treatments with LPS versus PBS on experimental day 5 shows DE genes. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis was performed on significantly DE genes (FDR < 0.01) in each condition (single and repeated LPS treatment). The canonical complement pathway showed significance in both conditions (p < 1E−06). The overlay represented corresponds to repeated treatment, and significant upregulated genes are shown in red; n > 3 mice. B, Gene transcript levels of complement pathway analyzed via sqRT-PCR in mouse brain on day 5 of the single or repeated treatment paradigm. The classical pathway initiator C1q is unresponsive to the LPS challenge. C3 is upregulated by both single and repeated LPS treatment. Itgam (complement receptor 3 [CR3]) and C4 transcripts are significantly upregulated only by the repeated treatment with LPS. n > 3 mice. n.s., Not significant. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. C, Quantification of TH-positive and NeuN-positive cells in the SNpc of C3-deficient (C3 KO) or wild-type (C3 WT) mice challenged repeatedly with PBS vehicle or LPS. The C3 KO mice showed no loss of TH-positive or NeuN-positive neurons compared with C3 WT animals; n ≥ 3 mice. n.s., Not significant. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001.
