Figure 4.
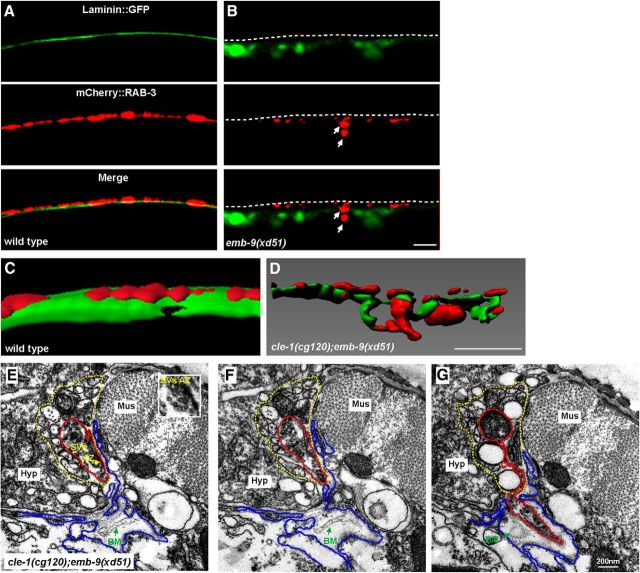
The integrity of the basement membrane is disrupted around the ectopic presynaptic sites. A, In wild-type, the smooth laminin::GFP sheet (green) is evenly distributed underneath presynapses labeled by Phmr-1b::mCherry::RAB-3 (red). Dashed lines indicate the dorsal cord region. B, Laminin::GFP is diffuse and fragmented in emb-9(xd51) animals (B′), and ectopic presynaptic boutons (indicated by arrows) are intermingled with Laminin::GFP. C, D, 3D reconstruction of Laminin::GFP and Phmr-1b::mCherry::RAB-3 in wild-type (C) and cle-1(cg120);emb-9(xd51) (D) animals. E, F, Two adjoining EM sections show where an ectopic presynaptic bouton is going to emerge from an existing presynaptic bouton (red lines) within the dorsal cord (yellow dashed lines). The loosely distributed BM (green arrows) is detached from muscle (blue lines) or neuron cells (red lines). Mus, Muscle; Hyp, hypodermal ridge. E, Insets, Clusters of synaptic vesicles and a darkly stained active zone. G, An ectopic bouton, originating from an existing presynapse, emerges from the dorsal cord (red line outlines synapses; yellow dashed line outlines dorsal cord). Scale bars, 5 μm.