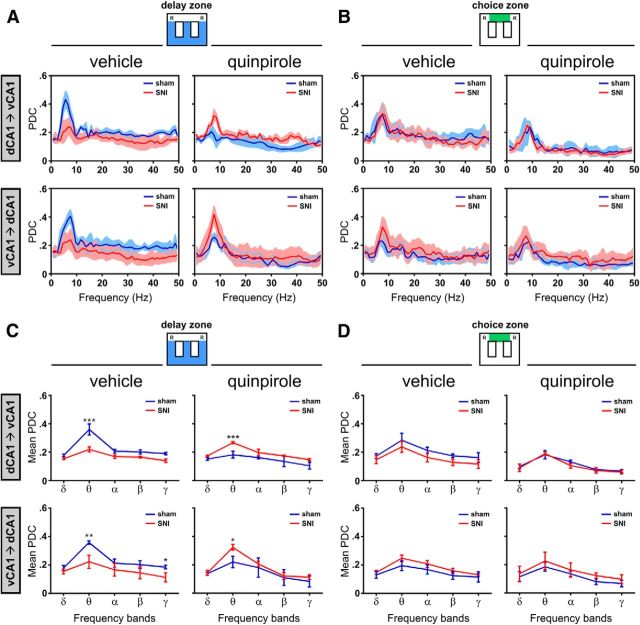
Figure 7.
Dorsoventral functional connectivity during maze navigation. A, B, Bidirectional traces of PDC across the spectral range of frequencies for both the sham and SNI groups before and after quinpirole administration. In all cases, there is a peak of PDC values in the θ range, reflecting that hippocampus dorsoventral functional connectivity is particularly important in this band of frequency. C, D, Bidirectional analysis of PDC per band of frequencies in both sham and SNI groups before and after quinpirole administration. The functional connectivity is only different between experimental groups during navigation in the delay zone, not in the choice zone. During navigation in the delay zone, quinpirole reversed the functional connectivity between experimental groups: before quinpirole, the sham animals presented the largest dorsoventral connectivity, whereas after quinpirole, the largest connectivity occurs in the SNI animals. Frequency bands: δ, 1–4 Hz; θ, 4–9 Hz; α, 9–15 Hz; β, 15–30 Hz; γ, 30–50 Hz. Values are presented as mean ± SEM. Comparisons between experimental groups are based on two-way ANOVA (group × frequency band), followed by post hoc Bonferroni. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.